Interventional Radiology ex-machina: impact of Artificial Intelligence on practice
- PMID: 33861421
- PMCID: PMC8050998
- DOI: 10.1007/s11547-021-01351-x
Interventional Radiology ex-machina: impact of Artificial Intelligence on practice
Abstract
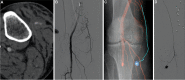
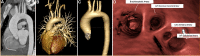
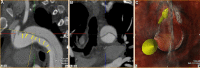
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of Informatics that uses algorithms to tirelessly process data, understand its meaning and provide the desired outcome, continuously redefining its logic. AI was mainly introduced via artificial neural networks, developed in the early 1950s, and with its evolution into "computational learning models." Machine Learning analyzes and extracts features in larger data after exposure to examples; Deep Learning uses neural networks in order to extract meaningful patterns from imaging data, even deciphering that which would otherwise be beyond human perception. Thus, AI has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare systems and clinical practice of doctors all over the world. This is especially true for radiologists, who are integral to diagnostic medicine, helping to customize treatments and triage resources with maximum effectiveness. Related in spirit to Artificial intelligence are Augmented Reality, mixed reality, or Virtual Reality, which are able to enhance accuracy of minimally invasive treatments in image guided therapies by Interventional Radiologists. The potential applications of AI in IR go beyond computer vision and diagnosis, to include screening and modeling of patient selection, predictive tools for treatment planning and navigation, and training tools. Although no new technology is widely embraced, AI may provide opportunities to enhance radiology service and improve patient care, if studied, validated, and applied appropriately.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence (AI); Augmented reality (AR); Deep learning (DL); Interventional radiology (IR); Machine learning (ML); Virtual reality (VR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S et al (2013) NIH Public Access 30:1234–1248. 10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010.QIN - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

