Extreme capsule is a bottleneck for ventral pathway
- PMID: 33861816
- PMCID: PMC8019950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2020.11.002
Extreme capsule is a bottleneck for ventral pathway
Abstract
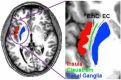
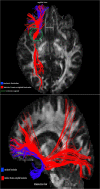
As neuroscience literature suggests, extreme capsule is considered a whiter matter tract. Nevertheless, it is not clear whether extreme capsule itself is an association fiber pathway or only a bottleneck for other association fibers to pass. Via our review, investigating anatomical position, connectivity and cognitive role of the bundles in extreme capsule, and by analyzing data from the dissection, it can be argued that extreme capsule is probably a bottleneck for the passage of uncinated fasciculus (UF) and inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF), and these fasciculi are responsible for the respective roles in language processing.
Keywords: Bottleneck; Diffusion tensor imaging; Extreme capsule; Inferior occipito-frontal fasciculus; Uncinated fasciculus; Ventral pathway of language.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Brain Research Organization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- de Almeida J.S., Lordier L., Zollinger B., Kunz N., Bastiani M., Gui L., Hüppi P.S. Music enhances structural maturation of emotional processing neural pathways in very preterm infants. Neuroimage. 2020;207 - PubMed
-
- Axer H., Klingner C.M., Prescher A. Fiber anatomy of dorsal and ventral language streams. Brain Lang. 2013;127(2):192–204. - PubMed
-
- Bajada C.J., Ralph M.A.L., Cloutman L.L. Transport for language south of the Sylvian fissure: the routes and history of the main tracts and stations in the ventral language network. Cortex. 2015;69:141–151. - PubMed
-
- Baldoncini M., Campero A., Cruz J.C.P., Recalde R., Parraga R., Gonzalez F.J.S., López P.G. Microsurgical anatomy and approaches to the cerebral central core. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:e23–e34. - PubMed
-
- Brauer J., Anwander A., Friederici A.D. Neuroanatomical prerequisites for language functions in the maturing brain. Cereb. Cortex. 2011;21(2):459–466. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
