Thrombotic microangiopathy in oncology - a review
- PMID: 33862523
- PMCID: PMC8065296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101081
Thrombotic microangiopathy in oncology - a review
Abstract
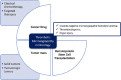
Thrombotic microangiopathy is a syndrome triggered by a wide spectrum of situations, some of which are specific to the Oncology setting. It is characterized by a Coombs-negative microangiopathic haemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia and organ injury, with characteristic pathological features, resulting from platelet microvascular occlusion. TMA is rare and its cancer-related subset even more so. TMA triggered by drugs is the most common within this group, including classic chemotherapy and the latest targeted therapies. The neoplastic disease itself and hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation could also be potential triggers. Evidence-based medical guidance in the management of cancer-related TMA is scarce and the previous knowledge about primary TMA is valuable to understand the disease mechanisms and the potential treatments. Given the wide spectrum of potential causes for TMA in cancer patients, the aim of this review is to gather the vast information available. For each entity, pathophysiology, clinical features, therapeutic approaches and prognosis will be covered.
Keywords: Cancer; Haematological malignancies; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Onco-nephrology; Thrombotic microangiopathies.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- George J.N., Nester C.M. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371(7):654–666. - PubMed
-
- Moschcowitz E. Hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries: a hitherto undescribed disease. Proc. N Y Pathol. Soc. 1924;24:21–24.
-
- Singer K., Bornstein F.P., Wile S.A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; hemorrhagic diathesis with generalized platelet thromboses. Blood. 1947;2(6):542–554. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo A., Faria B., Teixeira C., Carvalho F., Neto G., Santos J. Portuguese consensus document statement in diagnostic and management of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Port J. Nephrol. Hypert. 2018;32(3):211–232.
-
- Weitz I.C. Thrombotic Microangiopathy in cancer. Semin. Thromb Hemost. 2019;45(4):348–353. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources