Comparison between two cell collecting methods for liquid-based brush biopsies: a consecutive and retrospective study
- PMID: 33863321
- PMCID: PMC8052744
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-021-01557-5
Comparison between two cell collecting methods for liquid-based brush biopsies: a consecutive and retrospective study
Abstract
Background: This study compares two different cell collectors, the Orcellex Brush (rigid brush) and the Cytobrush GT (nylon brush), using liquid-based cytology. A comparison of their obtainment procedures was also considered. The aim was to determine the diagnostic accuracy for detection of malignancy in oral brush biopsies. PICO-Statement: In this consecutive and retrospective study we had as population of interests, patients with oral lesions, the intervention was the brush biopsy with two different cell collectors and the control was healthy oral mucosa. The outcome of the study was to compare both cell collectors.
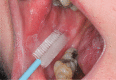
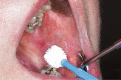
Methods: From 2009 to 2018, 2018 patients with oral lesions were studied using the nylon brush (666 cases) and rigid brush (1352 cases). In the first cohort five smears per patient were taken with the nylon brush, while each patient received one smear with the rigid brush in the second cohort. These were further processed in a liquid-based procedure. Cytological evaluations were categorised into 'negative', which were considered as negative, whereas 'doubtful', 'suspicious' and 'positive' cytological results were overall considered as positive for malignancy in comparison to the final histological diagnoses. Additionally, the clinical expenditure for each collector was estimated.
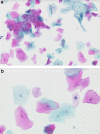
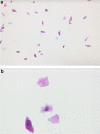
Results: 2018 clinically and histologically proven diagnoses were established, including 181 cases of squamous cell carcinomas, 524 lichen, 454 leukoplakias, 34 erythroplakias and 825 other benign lesions. The sensitivity and specificity of the nylon brush was 93.8% (95% CI 91.6-95.5%) and 94.2% (95% CI 91.8-95.5%) respectively, whereas it was 95.6% (95% CI 94.4-96.6%) and 84.9% (95% CI 83.8-87.5%) for the rigid brush. The temporal advantage using the plastic brushes was 4× higher in comparison to the nylon brush. The risk suffering from a malignant oral lesion when the result of the brushes was positive, suspicious, or doubtful was significantly high for both tests (nylon brush OR: 246.3; rigid brush OR: 121.5).
Conclusions: Both systems have a similar sensitivity, although only the rigid brush achieved a satisfactory specificity. Additional methods, such as DNA image cytometry, should also be considered to improve the specificity. Furthermore, the rigid brush proved to be more effective at taking a sufficient number of cells, whilst also being quicker and presenting less stress for the patient.
Keywords: Brush biopsy; Liquid-based cytology; Oral cancer; Squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Torsten W. Remmerbach is CEO of a dental healthcare supplier (DGOD Deutsche Gesellschaft für orale Diagnostika mbH, Leipzig, Germany). The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of nucleolar organizer regions (AgNORs) in brush biopsies of suspicious lesions of the oral cavity.Anal Cell Pathol. 2003;25(3):139-46. doi: 10.1155/2003/647685. Anal Cell Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12775918 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective, blinded comparison of cytology and DNA-image cytometry of brush biopsies for early detection of oral malignancy.Oral Oncol. 2013 May;49(5):420-6. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.12.006. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Oral Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23318121
-
Retrospective evaluation of the oral brush biopsy in daily dental routine - an effective way of early cancer detection.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Nov;26(11):6653-6659. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04620-9. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 35881238 Free PMC article.
-
[Usefulness of oral exfoliative cytology for the diagnosis of oral squamous dysplasia and carcinoma].Minerva Stomatol. 2004 Mar;53(3):77-86. Minerva Stomatol. 2004. PMID: 15107778 Review. Italian.
-
Liquid-based cytology in oral cavity squamous cell cancer.Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011 Apr;19(2):77-81. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e328343af10. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011. PMID: 21252668 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Oral Biopsies, Sample Types, and Detection Techniques Applied in Relation to Oral Cancer Detection.BioTech (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;11(1):5. doi: 10.3390/biotech11010005. BioTech (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35822813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the potential of interdental brush in oral cytology: a pilot study on sampling efficiency.BMC Oral Health. 2025 May 29;25(1):842. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06221-w. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40437465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woolgar JA, Triantafyllou A. Squamous cell carcinoma and precursor lesions: clinical pathology. Periodontol 2000. 2011;57(1):51–72. - PubMed
-
- https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/oralcav.html. Accessed 10 Jan 2021
-
- Reibel J, Gale N, Hille J, et al. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) IARC Press. 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

