Management and infection control practices in a Taiwanese radiology department during the COVID-19 outbreak
- PMID: 33863652
- PMCID: PMC8007533
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.03.012
Management and infection control practices in a Taiwanese radiology department during the COVID-19 outbreak
Abstract
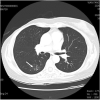
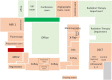
The radiology department was categorized as a "high risk area" during the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak in 2003 and is similarly considered a "high risk area" during the current coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. The purpose of infection control is to isolate patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 from uninfected people by utilizing separate equipment, spaces, and healthcare workers. Infection control measures should be prioritized to prevent the nosocomial spread of infection. We established a COVID-19 infection control team in our radiology department. The team's responsibilities include triaging patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, performing imaging and reporting, using dedicated equipment, disinfecting the equipment and the immediate environment, and staff scheduling.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Guidelines; Infection control; Radiology.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

