Pediatric Intern Clinical Exposure During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33863816
- PMCID: PMC8650022
- DOI: 10.1542/hpeds.2021-005899
Pediatric Intern Clinical Exposure During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background and objectives: Pediatric health care encounters declined during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, and pediatric residency programs have adapted trainee schedules to meet the needs of this changing clinical environment. We sought to evaluate the impact of the pandemic on pediatric interns' clinical exposure.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we quantified patient exposure among pediatric interns from a single large pediatric residency program at a freestanding children's hospital. Patient encounters and shifts per pediatric intern in the inpatient and emergency department settings were evaluated during the COVID-19 pandemic, from March to June 2020, as compared with these 3 months in 2019. Patient encounters by diagnosis were also evaluated.
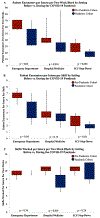
Results: The median number of patient encounters per intern per 2-week block declined on the pediatric hospital medicine service (37.5 vs 27.0; P < .001) and intensive care step-down unit (29.0 vs 18.8; P = .004) during the pandemic. No significant difference in emergency department encounters was observed (63.0 vs 40.5; P = .06). The median number of shifts worked per intern per 2-week block also decreased on the pediatric hospital medicine service (10.5 vs 9.5, P < .001). Across all settings, there were more encounters for screening for infectious disease and fewer encounters for respiratory illnesses.
Conclusions: Pediatric interns at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic were exposed to fewer patients and had reduced clinical schedules. Careful consideration is needed to track and supplement missed clinical experiences during the pandemic.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
Resident Clinical Experience During the Pandemic: What Has It Cost Us and What Have We Gained?Hosp Pediatr. 2021 Jul;11(7):e120-e122. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2021-005970. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Hosp Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33863815 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dong Y, Mo X, Hu Y, et al. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China. Pediatrics. 2020;145(6):e20200702. - PubMed
-
- Isba R, Edge R, Jenner R, Broughton E, Francis N, Butler J. Where have all the children gone? Decreases in paediatric emergency department attendances at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105(7):704. - PubMed
-
- Wilder JL, Parsons CR, Growdon AS, Toomey SL, Mansbach JM. Pediatric Hospitalizations During the COVID-19 Pandemic [published online ahead of print, 2020 Nov 3]. Pediatrics. 2020;e2020005983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

