multiSLIDE is a web server for exploring connected elements of biological pathways in multi-omics data
- PMID: 33863886
- PMCID: PMC8052434
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22650-x
multiSLIDE is a web server for exploring connected elements of biological pathways in multi-omics data
Abstract
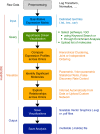
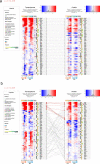
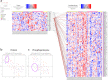
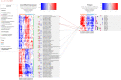
Quantitative multi-omics data are difficult to interpret and visualize due to large volume of data, complexity among data features, and heterogeneity of information represented by different omics platforms. Here, we present multiSLIDE, a web-based interactive tool for the simultaneous visualization of interconnected molecular features in heatmaps of multi-omics data sets. multiSLIDE visualizes biologically connected molecular features by keyword search of pathways or genes, offering convenient functionalities to query, rearrange, filter, and cluster data on a web browser in real time. Various querying mechanisms make it adaptable to diverse omics types, and visualizations are customizable. We demonstrate the versatility of multiSLIDE through three examples, showcasing its applicability to a wide range of multi-omics data sets, by allowing users to visualize established links between molecules from different omics data, as well as incorporate custom inter-molecular relationship information into the visualization. Online and stand-alone versions of multiSLIDE are available at https://github.com/soumitag/multiSLIDE .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

