Effect of magnesium and vitamin B6 supplementation on mental health and quality of life in stressed healthy adults: Post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 33864354
- PMCID: PMC9292249
- DOI: 10.1002/smi.3051
Effect of magnesium and vitamin B6 supplementation on mental health and quality of life in stressed healthy adults: Post-hoc analysis of a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
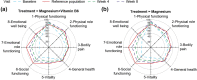
Magnesium status and vitamin B6 intake have been linked to mental health and/or quality of life (QoL). In an 8-week Phase IV randomised controlled study in individuals with low magnesemia and severe/extremely severe stress but who were otherwise healthy, greater stress reduction was achieved with magnesium combined with vitamin B6 than with magnesium alone. We present a previously unreported secondary analysis of the effect of magnesium, with and without vitamin B6, on depression, anxiety, and QoL. Adults with Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-42) stress subscale score >18 were randomised 1:1 to magnesium + vitamin B6 combination (Magne B6® ; daily dose 300 and 30 mg, respectively) or magnesium alone (Magnespasmyl® ; daily dose 300 mg). Outcomes included changes from baseline in DASS-42 depression and anxiety scores, and QoL (Short Form-36 Health Survey). DASS-42 anxiety and depression scores significantly improved from baseline to week 8 with both treatments, particularly during the first 4 weeks. Improvement in QoL continued over 8 weeks. Participants' perceived capacity for physical activity in daily life showed greater improvement with magnesium + vitamin B6 than magnesium alone (Week 4). In conclusion, magnesium supplementation, with or without vitamin B6, could provide a meaningful clinical benefit in daily life for individuals with stress and low magnesemia.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; magnesium supplementation; quality of life; stress; vitamin B6 supplementation.
© 2021 The Authors. Stress and Health published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Lionel Noah, Béatrice Bois De Fer, and Etienne Pouteau are employees of Sanofi‐Aventis. Gisèle Pickering reports consultancy fees from Sanofi, unrelated to this publication. André Mazur reports consultancy fees from Sanofi, unrelated to this publication. Louise Dye has received research funding from Sanofi and consultancy payments unrelated to this publication.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham, G. E. , Schwartz, U. D. , & Lubran, M. M. (1981). Effect of vitamin B‐6 on plasma and red blood cell magnesium levels in premenopausal women. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, 11(4), 333–336. http://www.annclinlabsci.org/cgi/content/abstract/11/4/333 - PubMed
-
- Briançon, S. , Boini, S. , Bertrais, S. , Guillemin, F. , Galan, P. , & Hercberg, S. (2011). Long‐term antioxidant supplementation has no effect on health‐related quality of life: The randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, primary prevention SU.VI.MAX trial. International Journal of Epidemiology, 40(6), 1605–1616. 10.1093/ije/dyr161 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

