Cytomegalovirus Viral Load Kinetics Predict Cytomegalovirus End-Organ Disease and Mortality After Hematopoietic Cell Transplant
- PMID: 33864371
- PMCID: PMC8366442
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab212
Cytomegalovirus Viral Load Kinetics Predict Cytomegalovirus End-Organ Disease and Mortality After Hematopoietic Cell Transplant
Abstract
Background: We investigatedthe association between time-averaged area under the curve (AAUC) of cytomegalovirus (CMV) viral load (VL) by day 100 and overall survival (OS) at 1-year after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT).
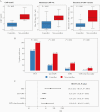
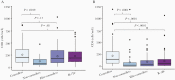
Methods: In a retrospective cohort study, including patients receiving HCT between June 2010 and December 2017 from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, AAUC was calculated for patients with detected VL. Patients were categorized into non-controllers (Q4) and controllers (Q1-Q3) using the highest AAUC quartile as cutoff. Cox models were used to estimate the association between AAUC and OS. Patients with non-detected CMV VL were categorized into elite-controllers (recipient+ [R+] or R-/donor+ [D+]) and R-/D-.
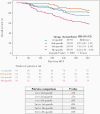
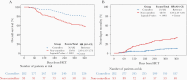
Results: The study (N = 952) included 282 controllers, 93 non-controllers, 275 elite-controllers, and 302 R-/D-. OS was 80.1% and 58.1% for controllers and non-controllers, respectively. In multivariable models, non-controllers had worse OS versus controllers (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] = 2.65; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.71-4.12). In landmark analyses, controllers had similar OS as elite-controllers (HR = 1.26; 95% CI, .83-1.91) or R-/D- (HR = 0.98; 95% CI, .64-1.5).
Conclusions: Non-controllers had worse OS 1-year post-HCT. Controllers had similar OS as elite-controllers or R-/D-. Future studies are needed to validate our AAUC cutoff across different cohorts and CMV management strategies.
Keywords: averaged area under the curve (AAUC); cytomegalovirus (CMV); end-organ disease (EOD); hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT); non-relapse mortality (NRM); overall survival (OS); viral load (VL).
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
Viral Load Kinetics: A Way to Assess Cumulative Effects of Cytomegalovirus on Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients.J Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 16;224(4):563-564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab213. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33864367 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boeckh M, Nichols WG. The impact of cytomegalovirus serostatus of donor and recipient before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the era of antiviral prophylaxis and preemptive therapy. Blood 2004; 103: 2003–8. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt-Hieber M, Labopin M, Beelen D, et al. . CMV serostatus still has an important prognostic impact in de novo acute leukemia patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Blood 2013; 122:3359–64. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt-Hieber M, Tridello G, Ljungman P, et al. . The prognostic impact of the cytomegalovirus serostatus in patients with chronic hematological malignancies after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a report from the Infectious Diseases Working Party of EBMT. Ann Hematol 2019; 98:1755–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

