Peptidylprolyl isomerase C (Ppic) regulates invariant Natural Killer T cell (iNKT) differentiation in mice
- PMID: 33864384
- PMCID: PMC8453708
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.202048924
Peptidylprolyl isomerase C (Ppic) regulates invariant Natural Killer T cell (iNKT) differentiation in mice
Abstract
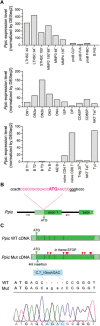
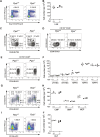
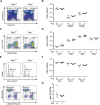
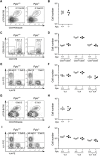
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase C (Ppic) is expressed in several bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic progenitors and in T-cell precursors. Since the expression profile of Ppic in the hematoimmune system was suggestive that it could play a role in hematopoiesis and/or T lymphocyte differentiation, we sought to test that hypothesis in vivo. Specifically, we generated a Ppic-deficient mouse model by targeting the endogenous locus by CRISPR/Cas9 and tested the requirement of Ppic in hematopoiesis. Several immune cell lineages covering BM progenitors, lymphocyte precursors, as well as mature cells at the periphery were analyzed. While most lineages were unaffected, invariant NKT (iNKT) cells were reduced in percentage and absolute cell numbers in the Ppic-deficient thymus. This affected the most mature stages in the thymus, S2 and S3, and the phenotype was maintained at the periphery. Additionally, immature transitional T1 and T2 B lymphocytes were increased in the Ppic-deficient spleen, but the phenotype was lost in mature B lymphocytes. In sum, our data show that Ppic is dispensable for myeloid cells, platelets, erythrocytes, αβ, and γδ T lymphocytes in vivo in the steady state, while being involved in B- and iNKT cell differentiation.
Keywords: Cyclophilin C; Hematopoiesis; Peptidylprolyl isomerase C; Ppic; T-cell development; Thymopoiesis.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Friedman, J. and Weissman, I., Two cytoplasmic candidates for immunophilin action are revealed by affinity for a new cyclophilin: one in the presence and one in the absence of CsA. Cell 1991. 66: 799–806. - PubMed
-
- Otsuka, M., Terada, Y., Yang, T., Nonoguchi, H., Tomita, K. and Marumo, F., Localization of cyclophilin A and cyclophilin C mRNA in murine kidney using RT‐PCR. Kidney Int. 1994. 45: 1340–1345. - PubMed
-
- Bram, R. J., Hung, D. T., Martin, P. K., Schreiber, S. L. and Crabtree, G. R., Identification of the immunophilins capable of mediating inhibition of signal transduction by cyclosporin A and FK506: roles of calcineurin binding and cellular location. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993. 13: 4760–4769. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

