IRAK2 Has a Critical Role in Promoting Feed-Forward Amplification of Epidermal Inflammatory Responses
- PMID: 33864770
- PMCID: PMC9423738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.03.019
IRAK2 Has a Critical Role in Promoting Feed-Forward Amplification of Epidermal Inflammatory Responses
Abstract
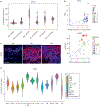
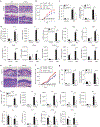
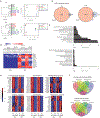
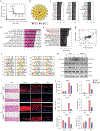
Many inflammatory skin diseases are characterized by altered epidermal differentiation. Whether this altered differentiation promotes inflammatory responses has been unknown. Here, we show that IRAK2, a member of the signaling complex downstream of IL-1 and IL-36, correlates positively with disease severity in both atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Inhibition of epidermal IRAK2 normalizes differentiation and inflammation in two mouse models of psoriasis- and atopic dermatitis-like inflammation. Specifically, we demonstrate that IRAK2 ties together proinflammatory and differentiation-dependent responses and show that this function of IRAK2 is specific to keratinocytes and acts through the differentiation-associated transcription factor ZNF750. Taken together, our findings suggest that IRAK2 has a critical role in promoting feed-forward amplification of inflammatory responses in skin through modulation of differentiation pathways and inflammatory responses.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
This work received support through BIOMAP (Biomarkers in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis), a project funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under Grant Agreement No. 821511. SW is coprincipal investigator of the German Atopic Eczema Registry TREATgermany; has received institutional research grants from Sanofi Deutschland GmbH, LEO Pharma, and La Roche Posay; has performed consultancies for Sanofi-Genzyme, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, AbbVie, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Kymab, and Novartis; has lectured at educational events sponsored by Sanofi-Genzyme, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, LEO Pharma, AbbVie, Novartis, and Galderma; and is involved in performing clinical trials with many pharmaceutical industries that manufacture drugs used for the treatment of psoriasis and atopic eczema. JMK has served on ad boards for AstraZeneca, Provention Bio, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Viela Bio, and Ventus Therapeutics and has grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and Q32 Bio. JEG has received honoraria from AnaptysBio, Bristol-Myers Squibb Celgene, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Almirall and research grants from Eli Lilly, Kyowa Kirin, Almirall, and Bristol-Myers Squibb Celgene. The other authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015;386:983–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR073196/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR060802/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR044882/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075047/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM086262/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR070590/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040312/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- L40 AR076139/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072773/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069071/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR080594/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075049/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR075043/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR072129/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

