Malnutrition and depression as predictors for 30-day unplanned readmission in older patient: a prospective cohort study to develop 7-point scoring system
- PMID: 33865312
- PMCID: PMC8052844
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02198-7
Malnutrition and depression as predictors for 30-day unplanned readmission in older patient: a prospective cohort study to develop 7-point scoring system
Abstract
Background: Readmission is related to high cost, high burden, and high risk for mortality in geriatric patients. A scoring system can be developed to predict the readmission of older inpatients to perform earlier interventions and prevent readmission.
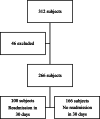
Methods: We followed prospectively inpatients aged 60 years and older for 30 days, with initial comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA) on admission in a tertiary referral centre. Patients were assessed with CGA tools consisting of FRAIL scale (fatigue, resistance, ambulation, illness, loss of weight), the 15-item Geriatric Depression Scale, Mini Nutritional Assessment short-form (MNA-SF), the Barthel index for activities of daily living (ADL), Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), caregiver burden based on 4-item Zarit Burden Index (ZBI), and cognitive problem with Abbreviated Mental Test (AMT). Demographic data, malignancy diagnosis, and number of drugs were also recorded. We excluded data of deceased patients and patients transferred to other hospitals. We conducted stepwise multivariate regression analysis to develop the scoring system.
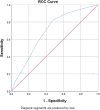
Results: Thirty-day unplanned readmission rate was 37.6 %. Among 266 patients, 64.7 % of them were malnourished, and 46.5 % of them were readmitted. About 24 % were at risk for depression or having depressed mood, and 53.1 % of them were readmitted. In multivariate analysis, nutritional status (OR 2.152, 95 %CI 1.151-4.024), depression status (OR 1.884, 95 %CI 1.071-3.314), malignancy (OR 1.863 95 %CI 1.005-3.451), and functional status (OR 1.584, 95 %CI 0.885-2.835) were included in derivation of 7 score system. The scoring system had maximum score of 7 and incorporated malnutrition (2 points), depression (2 points), malignancy (2 points), and dependent functional status (1 point). A score of 3 or higher suggested 82 % probability of readmission within 30 days following discharge. Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.694 (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: Malnutrition, depression, malignancy and functional problem are predictors for 30-day readmission. A practical CGA-based 7 scoring system had moderate accuracy and strong calibration in predicting 30-day unplanned readmission for older patients.
Keywords: Comprehensive geriatric assessment; Depression; Malnutrition; Predictive score; Readmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare(s) that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of 30-Day Readmission in Hospitalized Older Adults Using Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment and LACE Index and HOSPITAL Score.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 26;20(1):348. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010348. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612671 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of scoring system used before discharge to predict 30-day all-cause unplanned readmission in geriatric population: a prospective cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Mar 25;24(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04875-9. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38528454 Free PMC article.
-
Depressive symptoms and malnutrition are associated with other geriatric syndromes and increase risk for 30-Day readmission in hospitalized older adults: a prospective cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2022 Aug 2;22(1):634. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03343-6. BMC Geriatr. 2022. PMID: 35918652 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the elderly at risk for malnutrition. The Mini Nutritional Assessment.Clin Geriatr Med. 2002 Nov;18(4):737-57. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0690(02)00059-9. Clin Geriatr Med. 2002. PMID: 12608501 Review.
-
Comprehensive geriatric assessment prediction of postoperative complications in gastrointestinal cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Clin Interv Aging. 2018 Apr 24;13:723-736. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S155409. eCollection 2018. Clin Interv Aging. 2018. PMID: 29731614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing Sarcopenia, Frailty, and Malnutrition in Community-Dwelling Dependant Older Adults-An Exploratory Home-Based Study of an Underserved Group in Research.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 2;19(23):16133. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316133. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36498213 Free PMC article.
-
Malnutrition in Hospitalized Old Patients: Screening and Diagnosis, Clinical Outcomes, and Management.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 21;14(4):910. doi: 10.3390/nu14040910. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35215559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malnutrition Prevalence and Nutrient Intakes of Indonesian Older Adults in Institutionalized Care Setting: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies.Ann Nutr Metab. 2024;80(5):235-252. doi: 10.1159/000538790. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Ann Nutr Metab. 2024. PMID: 38636475 Free PMC article.
-
Residential Area Socioeconomic Deprivation is Associated with Physical Dependency and Polypharmacy in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: An Analysis of Health Administrative Data in Ireland.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022 Sep 2;15:1955-1963. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S380456. eCollection 2022. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36081581 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of 30-Day Readmission in Hospitalized Older Adults Using Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment and LACE Index and HOSPITAL Score.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 26;20(1):348. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010348. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soejono CH. The impact of “comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA)” implementation on the effectiveness and cost (CEA) of healthcare in an acute geriatric ward. Acta Med Indones. 2008;40:3–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

