Lyophilized alginate-based microspheres containing Lactobacillus fermentum D12, an exopolysaccharides producer, contribute to the strain's functionality in vitro
- PMID: 33865380
- PMCID: PMC8052780
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-021-01575-6
Lyophilized alginate-based microspheres containing Lactobacillus fermentum D12, an exopolysaccharides producer, contribute to the strain's functionality in vitro
Abstract
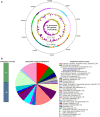
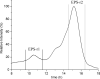
Lactobacillus (Limosilactobacillus) fermentum D12 is an exopolysaccharide (EPS) producing strain whose genome contains a putative eps operon. Whole-genome analysis of D12 was performed to disclose the essential genes correlated with activation of precursor molecules, elongation and export of the polysaccharide chain, and regulation of EPS synthesis. These included the genes required for EPS biosynthesis such as epsA, B, C, D and E, also gt, wzx, and wzy and those involved in the activation of the precursor molecules galE, galT and galU. Both the biosynthesis and export mechanism of EPS were proposed based on functional annotation. When grown on MRS broth with an additional 2% w/v glucose, L. fermentum D12 secreted up to 200 mg/L of a mixture of EPSs, whose porous structure was visualized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Structural information obtained by 1HNMR spectroscopy together with composition and linkage analyses, suggested the presence of at least two different EPSs, a branched heteropolysaccharide containing t-Glcp and 2,6-linked Galf, and glycogen. Since recent reports showed that polysaccharides facilitate the probiotic-host interactions, we at first sought to evaluate the functional potential of L. fermentum D12. Strain D12 survived simulated gastrointestinal tract (GIT) conditions, exhibited antibacterial activity against enteropathogenic bacteria, adhered to Caco-2 cells in vitro, and as such showed potential for in vivo functionality. The EPS crude extract positively influenced D12 strain capacity to survive during freeze-drying and to adhere to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins but did not interfere Caco-2 and mucin adherence when added at concentrations of 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 mg/mL. Since the viable bacterial count of free D12 cells was 3 logarithmic units lower after the exposure to simulated GIT conditions than the initial count, the bacterial cells had been loaded into alginate for viability improvement. Microspheres of D12 cells, which were previously analyzed at SEM, significantly influenced their survival during freeze-drying and in simulated GIT conditions. Furthermore, the addition of the prebiotic substrates mannitol and lactulose improved the viability of L. fermentum D12 in freeze-dried alginate microspheres during 1-year storage at 4 °C compared to the control.
Keywords: Eps cluster; Exopolysaccharides; Limosilactobacillus (Lactobacillus) fermentum; Prebiotic; Probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Limosilactobacillus fermentum strains MC1 and D12: Functional properties and exopolysaccharides characterization.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jul;273(Pt 2):133215. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133215. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38897515
-
Lactobacillus fermentum: Could EPS production ability be responsible for functional properties?Food Microbiol. 2020 Sep;90:103465. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103465. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32336376 Review.
-
Preparation, partial characterization and biological activity of exopolysaccharides produced from Lactobacillus fermentum S1.J Biosci Bioeng. 2020 Feb;129(2):206-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Biosci Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 31471140
-
Probiotic potential and safety properties of Limosilactobacillus fermentum A51 with high exopolysaccharide production.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 21;16:1498352. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1498352. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39906755 Free PMC article.
-
Limosilactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: Clinical Potential of a Probiotic Strain Isolated from Human Milk.Nutrients. 2023 May 6;15(9):2207. doi: 10.3390/nu15092207. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Limosilactobacillus fermentum ING8, a Potential Multifunctional Non-Starter Strain with Relevant Technological Properties and Antimicrobial Activity.Foods. 2022 Feb 26;11(5):703. doi: 10.3390/foods11050703. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35267336 Free PMC article.
-
A Lactic Acid Bacteria Consortium Impacted the Content of Casein-Derived Biopeptides in Dried Fresh Cheese.Molecules. 2021 Dec 28;27(1):160. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010160. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011392 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Milk Microbiota Produces Potential Therapeutic Biomolecules and Shapes the Intestinal Microbiota of Infants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 19;23(22):14382. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214382. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430861 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of exopolysaccharide-producing Enterobacter aerogenes NJ1023 and its cadaverine biosynthesis promotion.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 27;14:1200123. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1200123. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37577413 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of growth of Levilactobacillus brevis SP 48 and in vitro evaluation of the effect of viable cells and high molecular weight potential postbiotics on Helicobacter pylori.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 31;10:1007004. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1007004. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36394050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bengoa A, Goretti Llamas M, Irapordaa C, Dueñas MT, Abraham AG, Garrote GL. Impact of growth temperature on exopolysaccharide production and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus paracasei strains isolated from kefir grains. Food Microbiol. 2018;69:212–218. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.08.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

