Molecular Mechanism of Nramp-Family Transition Metal Transport
- PMID: 33865868
- PMCID: PMC8292206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166991
Molecular Mechanism of Nramp-Family Transition Metal Transport
Abstract
The Natural resistance-associated macrophage protein (Nramp) family of transition metal transporters enables uptake and trafficking of essential micronutrients that all organisms must acquire to survive. Two decades after Nramps were identified as proton-driven, voltage-dependent secondary transporters, multiple Nramp crystal structures have begun to illustrate the fine details of the transport process and provide a new framework for understanding a wealth of preexisting biochemical data. Here we review the relevant literature pertaining to Nramps' biological roles and especially their conserved molecular mechanism, including our updated understanding of conformational change, metal binding and transport, substrate selectivity, proton transport, proton-metal coupling, and voltage dependence. We ultimately describe how the Nramp family has adapted the LeuT fold common to many secondary transporters to provide selective transition-metal transport with a mechanism that deviates from the canonical model of symport.
Keywords: APC superfamily; iron homeostasis; manganese; proton-coupled transport; secondary transporter.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

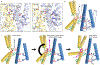
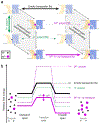
Similar articles
-
Unique structural features in an Nramp metal transporter impart substrate-specific proton cotransport and a kinetic bias to favor import.J Gen Physiol. 2019 Dec 2;151(12):1413-1429. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912428. Epub 2019 Oct 16. J Gen Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31619456 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure and Conformational Change Mechanism of a Bacterial Nramp-Family Divalent Metal Transporter.Structure. 2016 Dec 6;24(12):2102-2114. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.09.017. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27839948 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane helix 6b links proton and metal release pathways and drives conformational change in an Nramp-family transition metal transporter.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 31;295(5):1212-1224. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011336. Epub 2019 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31882536 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in structure-function analyses of Nramp proton-dependent metal-ion transporters.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;84(6):960-78. doi: 10.1139/o06-193. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17215883 Review.
-
Nutritional immunity: homology modeling of Nramp metal import.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;946:335-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0106-3_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 21948377 Review.
Cited by
-
Ion and lipid orchestration of secondary active transport.Nature. 2024 Feb;626(8001):963-974. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07062-3. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38418916 Review.
-
Global cellular proteo-lipidomic profiling of diverse lysosomal storage disease mutants using nMOST.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 20:2024.03.26.586828. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.26.586828. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 24;11(4):eadu5787. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu5787. PMID: 38585873 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A weak allele of OsNRAMP5 for safer rice.J Exp Bot. 2022 Oct 18;73(18):6009-6012. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac323. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 36255375 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
BrpNAC895 and BrpABI449 coregulate the transcription of the afflux-type Cd transporter BrpHMA2 in Brassica parachinensis.Hortic Res. 2022 Feb 19;9:uhac044. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac044. Online ahead of print. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 35184182 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide co-expression network analysis revealed ZmNRAMP6-mediated regulatory pathway involved in maize tolerance to lead stress.Theor Appl Genet. 2023 May 4;136(5):122. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04371-5. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 37142873
References
-
- Posey JE, Gherardini FC. Lack of a role for iron in the Lyme disease pathogen. Science. 2000;288:1651–3. - PubMed
-
- Archibald F. Lactobacillus plantarum, an organism not requiring iron. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 1983;19:29–32.
-
- Kolber ZS, Barber RT, Coale KH, Fitzwateri SE, Greene RM, Johnson KS, et al. Iron limitation of phytoplankton photosynthesis in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Nature. 1994;371:145–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

