The fight against COVID-19: Striking a balance in the renin-angiotensin system
- PMID: 33865979
- PMCID: PMC8049177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.04.006
The fight against COVID-19: Striking a balance in the renin-angiotensin system
Abstract
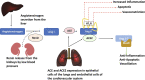
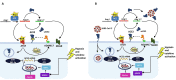
The novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) enters host cells by interacting with membrane-bound angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a vital element in the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which regulates blood pressure, fluid balance, and cardiovascular functions. We herein evaluate existing evidence for the molecular alterations within the RAS pathway (e.g., ACE2 and angiotensin II) during SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). This includes reports regarding potential effect of RAS blockade (e.g., ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers) on ACE2 expression and clinical outcomes in patients with co-morbidities commonly treated with these agents. The collective evidence suggests a dual role for ACE2 in COVID-19, depending on the stage of infection and the coexisting diseases in individual patients. This information is further discussed with respect to potential therapeutic strategies targeting RAS for COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: Angiotensin II (Ang II); Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2); COVID-19; RAS blockade; Renin-angiotensin system (RAS); SARS-CoV-2.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme 2 and Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19: An Update.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021 Mar;28(2):129-139. doi: 10.1007/s40292-021-00439-9. Epub 2021 Feb 26. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021. PMID: 33635533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II Promotes SARS-CoV-2 Infection via Upregulation of ACE2 in Human Bronchial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 4;23(9):5125. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095125. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563515 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II receptors: Impact for COVID-19 severity.Dermatol Ther. 2020 Nov;33(6):e13989. doi: 10.1111/dth.13989. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Dermatol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32645228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):L325-L336. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00189.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32639866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of Membrane-bound Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Receptor has a Pivotal Role in COVID-19 Immunopathology.Curr Drug Targets. 2021;22(3):254-281. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666201020154033. Curr Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33081670 Review.
Cited by
-
Papaverine, a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of COVID-19 patients with underlying cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).Drug Dev Res. 2022 Sep;83(6):1246-1250. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21961. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Drug Dev Res. 2022. PMID: 35706384 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Antioxidants for the Neuro-Therapeutic Management of COVID-19.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;10(6):971. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060971. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Assessment of the Binding and Neutralisation Activity of Bispecific Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants.Antib Ther. 2022 Dec 29;6(1):49-58. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbac032. eCollection 2023 Jan. Antib Ther. 2022. PMID: 36683765 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between the renin-angiotensin, complement and kallikrein-kinin systems in inflammation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Jul;22(7):411-428. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00634-8. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34759348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary fibrosis from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic interventions: lessons from post-COVID-19 patients.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;193:114812. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114812. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34687672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

