New Insights and Novel Therapeutic Potentials for Macrophages in Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 33866463
- PMCID: PMC8460536
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-021-01467-2
New Insights and Novel Therapeutic Potentials for Macrophages in Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
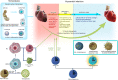
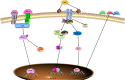
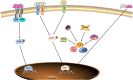
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) has long been the leading cause of death worldwide, and myocardial infarction (MI) accounts for the greatest proportion of CVD. Recent research has revealed that inflammation plays a major role in the pathogenesis of CVD and other manifestations of atherosclerosis. Overwhelming evidence supports the view that macrophages, as the basic cell component of the innate immune system, play a pivotal role in atherosclerosis initiation and progression. Limited but indispensable resident macrophages have been detected in the healthy heart; however, the number of cardiac macrophages significantly increases during cardiac injury. In the early period of initial cardiac damage (e.g., MI), numerous classically activated macrophages (M1) originating from the bone marrow and spleen are rapidly recruited to damaged sites, where they are responsible for cardiac remodeling. After the inflammatory stage, the macrophages shift toward an alternatively activated phenotype (M2) that promotes cardiac repair. In addition, extensive studies have shown the therapeutic potential of macrophages as targets, especially for emerging nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery systems. In the present review, we focused on the role of macrophages in the development and progression of MI, factors regulating macrophage activation and function, and the therapeutic potential of macrophages in MI.
Keywords: cardiac repair; macrophages; myocardial infarction; polarization; therapeutic strategies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

