Von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 activity as clinical severity markers in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 33866481
- PMCID: PMC8053027
- DOI: 10.1007/s11239-021-02457-9
Von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 activity as clinical severity markers in patients with COVID-19
Abstract
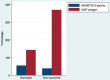
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) increases thrombotic risk. The mechanisms that lead to this prothrombotic state are not well established. The main aim was to evaluate the von Willebrand factor (VWF) antigen and plasma ADAMTS13 activity as endothelial injury markers in COVID-19. We present a prospective study in COVID-19 patients recruited in our institution. VWF antigen, ADAMTS13 activity, D-dimer, and fibrinogen were measured during the first week once COVID-19 was diagnosed. Fifty COVID-19 inpatients [44% in the intensive care unit (ICU)] and 102 COVID-19 outpatients were enrolled. Thirty age and gender matched non-COVID-19 ward inpatients and 30 non-COVID-19 healthy individuals were recruited. The COVID-19 inpatients had higher D-dimer, fibrinogen, and VWF antigen levels and a lower ADAMTS13 activity compared with the COVID-19 outpatients (p < 0.05). ICU patients had higher D-dimer and VWF antigen levels compared with the ward patients and the lowest ADAMTS13 activity (p < 0.05). An imbalance in VWF antigen/ADAMTS13 ratio was observed in COVID-19, reaching the highest in ICU patients. In contrast to other ward non-COVID-19 inpatients, a significative reduction in ADAMTS13 activity was observed in all COVID-19 patients. There is an increase in VWF antigen and an ADAMTS13 activity reduction in COVID-19 related to disease severity and could predict poor clinical outcomes. The ADAMTS13 activity reduction could be a marker associated with COVID-19 compared to other non-critical medical conditions.
Keywords: ADAMTS13; COVID-19; Endothelial dysfunction; Hypercoagulability; Von Willebrand factor.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous