Clinically Significant Drug Interactions Between Psychotropic Agents and Repurposed COVID-19 Therapies
- PMID: 33866523
- PMCID: PMC8053373
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-021-00811-2
Clinically Significant Drug Interactions Between Psychotropic Agents and Repurposed COVID-19 Therapies
Abstract
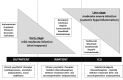
As many patients with underlying psychiatric disorders may be infected with COVID-19, and COVID-19-affected subjects may frequently experience a new onset of psychiatric manifestations, concomitant use of psychotropic medications and COVID-19 therapies is expected to be highly likely and raises concerns of clinically relevant drug interactions. In this setting, four major mechanisms responsible for drug interactions involving psychotropic agents and COVID-19 therapies may be identified: (1) pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions mainly acting on cytochrome P450; (2) pharmacodynamic drug-drug interactions resulting in additive or synergistic toxicity; (3) drug-disease interactions according to stage and severity of the disease; and (4) pharmacogenetic issues associated with polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. In this review, we summarise the available literature on relevant drug interactions between psychotropic agents and COVID-19 therapies, providing practical clinical recommendations and potential management strategies according to severity of illness and clinical scenario.
Conflict of interest statement
Federico Pea participated in the speaker bureau for Angelini, Basilea Pharmaceutica Gilead, Hikma, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer and Sanofi Aventis, and in an advisory board for Angelini, Basilea Pharmaceutica, Correvio, Gilead, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer and Thermo–Fisher. Milo Gatti and Fabrizio De Ponti have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. WHO Director-General’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at.... Accessed 22 Dec 2020.
-
- WHO. Virtual press conference on COVID-19, 11 March 2020. Available from: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus.... Accessed 22 Dec 2020.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. COVID-19 situation update worldwide. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases. Accessed 22 Dec 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

