Reduced humoral response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients without prior exposure to the virus
- PMID: 33866672
- PMCID: PMC8250589
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16615
Reduced humoral response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients without prior exposure to the virus
Abstract
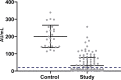
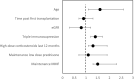
COVID-19 is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in transplant recipients. There are no efficacy data available regarding these patients with any of the available SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. We analyzed the humoral response following full vaccination with the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) in 136 kidney transplant recipients, and compared it to 25 controls. In order to exclude prior exposure to the virus, only participants with negative serology to SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein were included. All controls developed a positive response to spike protein, while only 51 of 136 transplant recipients (37.5%) had positive serology (p < .001). Mean IgG anti-spike level was higher in the controls (31.05 [41.8] vs. 200.5 [65.1] AU/mL, study vs. control, respectively, p < .001). Variables associated with null humoral response were older age (odds ratio 1.66 [95% confidence interval 1.17-2.69]), high-dose corticosteroids in the last 12 months (1.3 [1.09-1.86]), maintenance with triple immunosuppression (1.43 [1.06-2.15]), and regimen that includes mycophenolate (1.47 [1.26-2.27]). There was a similar rate of side effects between controls and recipients, and no correlation was found between the presence of symptoms and seroconversion. Our findings suggest that most kidney transplant recipients remain at high risk for COVID-19 despite vaccination. Further studies regarding possible measures to increase recipient's response to vaccination are required.
Keywords: clinical research/practice; immunosuppressant; kidney transplantation/nephrology; vaccine.
© 2021 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reduced humoral response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients without prior exposure to the virus: No cause for alarm.Am J Transplant. 2021 Aug;21(8):2908. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16687. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 33998136 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination, Immune Responses, and Antibody Testing in Immunosuppressed Populations: Tip of the Iceberg.Transplantation. 2021 Sep 1;105(9):1911-1913. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003859. Transplantation. 2021. PMID: 34144554 No abstract available.
-
Serological response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients depends on prior exposure to SARS-CoV-2.Am J Transplant. 2021 Nov;21(11):3806-3807. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16726. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34153162 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

