Precise engineering of hybrid molecules-loaded macromolecular nanoparticles shows in vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy toward the treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer cells
- PMID: 33866910
- PMCID: PMC8079022
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1902022
Precise engineering of hybrid molecules-loaded macromolecular nanoparticles shows in vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy toward the treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer cells
Abstract
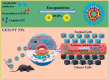
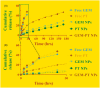
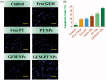
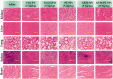
Cancers continue to be the second leading cause of death worldwide. Despite the development and improvement of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy in cancer management, effective tumor ablation strategies are still in need due to high cancer patient mortality. Hence, we have established a new approach to achieve treatment-actuated modifications in a tumor microenvironment by using synergistic activity between two potential anticancer drugs. Dual drug delivery of gemcitabine (GEM) and cisplatin (PT) exhibits a great anticancer potential, as GEM enhances the effect of PT treatment of human cells by providing stability of the microenvironment. However, encapsulation of GEM and PT fanatical by methoxypoly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(D, L-lactic acid) (PEG-PLA in termed as NPs) is incompetent owing to unsuitability between the binary Free GEM and PT core and the macromolecular system. Now, we display that PT can be prepared by hydrophobic coating of the dual drug centers with dioleoylphosphatidic acid (DOPA). The DOPA-covered PT can be co-encapsulated in PLGA NPs alongside GEM to stimulate excellent anticancer property. The occurrence of the PT suggestively enhanced the encapsulations of GEM into PLGA NPs (GEM-PT NPs). Further, the morphology of GEM NPs, PT NPs, and GEM-PT NPs and nanoparticle size was examined by transmission microscopy (TEM), respectively. Furthermore GEM-PT NPs induced significant apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 and SUNE1 cancer cells by in vitro. The morphological observation and apoptosis were confirmed by the various biochemical assays (AO-EB, nuclear staining, and annexin V-FITC). In a xenograft model of nasopharyngeal cancer, this nanotherapy shows a durable inhibition of tumor progression upon the administration of a tolerable dose. Our results suggest that a macromolecular hydrophobic and highly toxic drug can be rationally converted into a pharmacologically efficient and self-deliverable of nanotherapy.
Keywords: Combinational delivery; apoptosis; in vivo antitumor efficacy; nasopharyngeal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Co-drug delivery of regorafenib and cisplatin with amphiphilic copolymer nanoparticles: enhanced in vivo antitumor cancer therapy in nursing care.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):1319-1328. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1815897. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32936009 Free PMC article.
-
Combinational dual drug delivery system to enhance the care and treatment of gastric cancer patients.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):1491-1500. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1822460. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 33100060 Free PMC article.
-
Layer-by-layer nanoparticles co-loading gemcitabine and platinum (IV) prodrugs for synergistic combination therapy of lung cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Sep 5;11:2631-2642. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S143047. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 28919713 Free PMC article.
-
Gemcitabine: immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive role in the tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1536428. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1536428. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40270972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances and prospects in gemcitabine drug delivery systems.Int J Pharm. 2021 Jan 5;592:120043. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120043. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33152476 Review.
Cited by
-
Cisplatin-Based Combination Therapy for Enhanced Cancer Treatment.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(7):473-491. doi: 10.2174/0113894501294182240401060343. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38591210 Review.
-
Synergistic effect of Hsp90 inhibitor ginkgolic acids C15꞉1 combined with paclitaxel on nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Aug 28;48(8):1128-1135. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230061. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37875353 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Agrawal M, Saraf S, Saraf S, et al. (2018). Nose-to-brain drug delivery: an update on clinical challenges and progress towards approval of anti-Alzheimer drugs. J Control Release 281:139–77. - PubMed
-
- Balaji S, Mohamed Subarkhan MK, Ramesh R, et al. (2020). Synthesis and structure of arene Ru(II) N∧O-chelating complexes: in vitro cytotoxicity and cancer cell death mechanism. Organometallics 39:1366–75.
-
- Delplace V, Couvreur P, Nicolas J. (2014). Recent trends in the design of anticancer polymer prodrug nanocarriers. Polym Chem 5:1529–44.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
