Biosensing strategies for the electrochemical detection of viruses and viral diseases - A review
- PMID: 33867035
- PMCID: PMC9186435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.338384
Biosensing strategies for the electrochemical detection of viruses and viral diseases - A review
Abstract
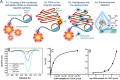
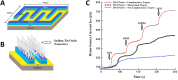
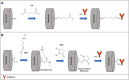
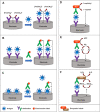
Viruses are the causing agents for many relevant diseases, including influenza, Ebola, HIV/AIDS, and COVID-19. Its rapid replication and high transmissibility can lead to serious consequences not only to the individual but also to collective health, causing deep economic impacts. In this scenario, diagnosis tools are of significant importance, allowing the rapid, precise, and low-cost testing of a substantial number of individuals. Currently, PCR-based techniques are the gold standard for the diagnosis of viral diseases. Although these allow the diagnosis of different illnesses with high precision, they still present significant drawbacks. Their main disadvantages include long periods for obtaining results and the need for specialized professionals and equipment, requiring the tests to be performed in research centers. In this scenario, biosensors have been presented as promising alternatives for the rapid, precise, low-cost, and on-site diagnosis of viral diseases. This critical review article describes the advancements achieved in the last five years regarding electrochemical biosensors for the diagnosis of viral infections. First, genosensors and aptasensors for the detection of virus and the diagnosis of viral diseases are presented in detail regarding probe immobilization approaches, detection methods (label-free and sandwich), and amplification strategies. Following, immunosensors are highlighted, including many different construction strategies such as label-free, sandwich, competitive, and lateral-flow assays. Then, biosensors for the detection of viral-diseases-related biomarkers are presented and discussed, as well as point of care systems and their advantages when compared to traditional techniques. Last, the difficulties of commercializing electrochemical devices are critically discussed in conjunction with future trends such as lab-on-a-chip and flexible sensors.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Biosensors; Electrochemistry; Genosensor; Immunosensor; Viral diseases.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Webster R.G., Bean W.J., Gorman O.T., Chambers T.M., Kawaoka Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992;56 http://mmbr.asm.org/content/56/1/152.abstract 152 LP – 179. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

