Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in COVID-19
- PMID: 33867130
- PMCID: PMC7997307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.03.006
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in COVID-19
Abstract
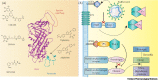
Latest research shows that SERPINE1 overexpression has an important role in Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19)-associated coagulopathy leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). However, ways to target this protein remain elusive. In this forum, we discuss recent evidence linking SERPINE1 with COVID-19-related ARDS and summarize the available data on inhibitors of this target.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors are employees of Evotec (UK) Ltd.
Figures
Comment on
-
Complement activation and endothelial perturbation parallel COVID-19 severity and activity.J Autoimmun. 2021 Jan;116:102560. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102560. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33139116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellici T.F., et al. Small-molecule modulators of serine protease inhibitor proteins (serpins) Drug Discov. Today. 2021;26:442–454. - PubMed
-
- Wu K., et al. The cleavage and inactivation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 by neutrophil elastase: the evaluation of its physiologic relevance in fibrinolysis. Blood. 1995;86:1056–1061. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y.P., et al. Analysis of thrombotic factors in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2006;96:100–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

