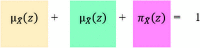Decision support system for ranking relevant indicators for reopening strategies following COVID-19 lockdowns
- PMID: 33867586
- PMCID: PMC8035617
- DOI: 10.1007/s11135-021-01129-3
Decision support system for ranking relevant indicators for reopening strategies following COVID-19 lockdowns
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Decision support system for ranking relevant indicators for reopening strategies following COVID-19 lockdowns.Qual Quant. 2022;56(2):493. doi: 10.1007/s11135-021-01154-2. Epub 2021 May 3. Qual Quant. 2022. PMID: 33967348 Free PMC article.
Abstract
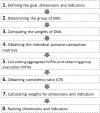
The pandemic caused by the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus forced governments around the world to impose lockdowns, which mostly involved restricting non-essential activities. Once the rate of infection is manageable, governments must implement strategies that reverse the negative effects of the lockdowns. A decision support system based on fuzzy theory and multi-criteria decision analysis principles is proposed to investigate the importance of a set of key indicators for post-COVID-19 reopening strategies. This system yields more reliable results because it considers the hesitation and experience of decision makers. By including 16 indicators that are utilized by international organizations for comparing, ranking, or investigating countries, our results suggest that governments and policy makers should focus their efforts on reducing violence, crime and unemployment. The provided methodology illustrates the suitability of decision science tools for tackling complex and unstructured problems, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Governments, policy makers and stakeholders might find in this work scientific-based guidelines that facilitate complex decision-making processes.
Keywords: Analytic hierarchy process; COVID-19; Decision support system; Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets; Lockdowns.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullah L, Najib L. A new preference scale MCDM method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and the analytic hierarchy process. Soft Comput. 2016;20:511–523. doi: 10.1007/s00500-014-1519-y. - DOI
-
- Aboal D, Lanzilotta B, Dominguez M, Vairo M. The cost of crime and violence in five Latin American countries. Eur. J. Crim. Policy Res. 2016;22:689–711. doi: 10.1007/s10610-015-9295-5. - DOI
-
- Amadeo, K.: Retail sales and its components. The balance Pub. https://www.thebalance.com/what-is-retail-sales-3305722 (2020). Accessed 26 August 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous