Neuro-Nano Interfaces: Utilizing Nano-Coatings and Nanoparticles to Enable Next-Generation Electrophysiological Recording, Neural Stimulation, and Biochemical Modulation
- PMID: 33867903
- PMCID: PMC8049593
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201700239
Neuro-Nano Interfaces: Utilizing Nano-Coatings and Nanoparticles to Enable Next-Generation Electrophysiological Recording, Neural Stimulation, and Biochemical Modulation
Abstract
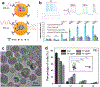
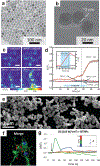
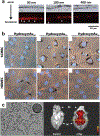
Neural interfaces provide a window into the workings of the nervous system-enabling both biosignal recording and modulation. Traditionally, neural interfaces have been restricted to implanted electrodes to record or modulate electrical activity of the nervous system. Although these electrode systems are both mechanically and operationally robust, they have limited utility due to the resultant macroscale damage from invasive implantation. For this reason, novel nanomaterials are being investigated to enable new strategies to chronically interact with the nervous system at both the cellular and network level. In this feature article, the use of nanomaterials to improve current electrophysiological interfaces, as well as enable new nano-interfaces to modulate neural activity via alternative mechanisms, such as remote transduction of electromagnetic fields are explored. Specifically, this article will review the current use of nanoparticle coatings to enhance electrode function, then an analysis of the cutting-edge, targeted nanoparticle technologies being utilized to interface with both the electrophysiological and biochemical behavior of the nervous system will be provided. Furthermore, an emerging, specialized-use case for neural interfaces will be presented: the modulation of the blood-brain barrier.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; brain; nanoparticle; neural interface; neurostimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


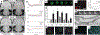
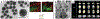
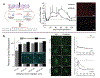
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
