Modeling Working Memory in a Spiking Neuron Network Accompanied by Astrocytes
- PMID: 33867939
- PMCID: PMC8044545
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.631485
Modeling Working Memory in a Spiking Neuron Network Accompanied by Astrocytes
Abstract
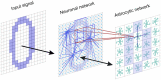
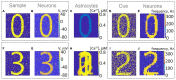
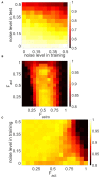
We propose a novel biologically plausible computational model of working memory (WM) implemented by a spiking neuron network (SNN) interacting with a network of astrocytes. The SNN is modeled by synaptically coupled Izhikevich neurons with a non-specific architecture connection topology. Astrocytes generating calcium signals are connected by local gap junction diffusive couplings and interact with neurons via chemicals diffused in the extracellular space. Calcium elevations occur in response to the increased concentration of the neurotransmitter released by spiking neurons when a group of them fire coherently. In turn, gliotransmitters are released by activated astrocytes modulating the strength of the synaptic connections in the corresponding neuronal group. Input information is encoded as two-dimensional patterns of short applied current pulses stimulating neurons. The output is taken from frequencies of transient discharges of corresponding neurons. We show how a set of information patterns with quite significant overlapping areas can be uploaded into the neuron-astrocyte network and stored for several seconds. Information retrieval is organized by the application of a cue pattern representing one from the memory set distorted by noise. We found that successful retrieval with the level of the correlation between the recalled pattern and ideal pattern exceeding 90% is possible for the multi-item WM task. Having analyzed the dynamical mechanism of WM formation, we discovered that astrocytes operating at a time scale of a dozen of seconds can successfully store traces of neuronal activations corresponding to information patterns. In the retrieval stage, the astrocytic network selectively modulates synaptic connections in the SNN leading to successful recall. Information and dynamical characteristics of the proposed WM model agrees with classical concepts and other WM models.
Keywords: astrocyte; delayed activity; neuron-astrocyte interaction; spiking neural network; working memory.
Copyright © 2021 Gordleeva, Tsybina, Krivonosov, Ivanchenko, Zaikin, Kazantsev and Gorban.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Working memory depends on the excitatory-inhibitory balance in neuron-astrocyte network.Chaos. 2023 Jan;33(1):013127. doi: 10.1063/5.0126890. Chaos. 2023. PMID: 36725632
-
Information Encoding in Bursting Spiking Neural Network Modulated by Astrocytes.Entropy (Basel). 2023 May 1;25(5):745. doi: 10.3390/e25050745. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238500 Free PMC article.
-
A digital neuromorphic system for working memory based on spiking neuron-astrocyte network.Neural Netw. 2025 Feb;182:106934. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106934. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Neural Netw. 2025. PMID: 39622098
-
Essential Role of Astrocytes in Learning and Memory.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1899. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031899. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From in silico astrocyte cell models to neuron-astrocyte network models: A review.Brain Res Bull. 2018 Jan;136:76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.01.027. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 28189516 Review.
Cited by
-
Robust and brain-like working memory through short-term synaptic plasticity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Dec 27;18(12):e1010776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010776. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36574424 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IP3 receptors and SERCA pumps in restoring working memory under amyloid β induced Alzheimer's disease: a modeling study.Front Comput Neurosci. 2025 Jul 22;19:1643547. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2025.1643547. eCollection 2025. Front Comput Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40765919 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducing the Few-Shot Learning Capabilities of the Visual Ventral Pathway Using Vision Transformers and Neural Fields.Brain Sci. 2025 Aug 19;15(8):882. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15080882. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40867213 Free PMC article.
-
The "psychiatric" neuron: the psychic neuron of the cerebral cortex, revisited.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Mar 18;18:1356674. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1356674. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38562227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of working memory duration by synaptic and astrocytic mechanisms.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Oct 3;18(10):e1010543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010543. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36191056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amit D. (1995). Modeling Brain Functions: The World of Attractor Neural Networks. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

