Gray Matter Atrophy in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Voxel-Based Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33867968
- PMCID: PMC8044397
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.627919
Gray Matter Atrophy in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Voxel-Based Meta-Analysis
Abstract
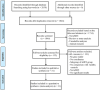
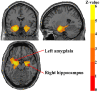
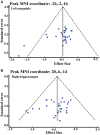
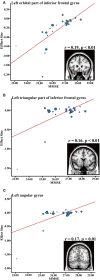
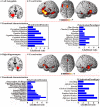
Background: Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) has been widely used to investigate structural alterations in amnesia mild cognitive impairment (aMCI). However, inconsistent results have hindered our understanding of the exact neuropathology related to aMCI. Objectives: Our aim was to systematically review the literature reporting VBM on aMCI to elucidate consistent gray matter alterations, their functional characterization, and corresponding co-activation patterns. Methods: The PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE databases were searched for VBM studies on aMCI published from inception up to June 2020. Peak coordinates were extracted from clusters that showed significant gray matter differences between aMCI patients and healthy controls (HC). Meta-analysis was performed using seed-based d mapping with the permutation of subject images (SDM-PSI), a newly improved meta-analytic method. Functional characterization and task-based co-activation patterns using the BrainMap database were performed on significant clusters to explore their functional roles. Finally, VBM was performed based on the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset to further support the findings. Results: A total of 31 studies with 681 aMCI patients and 837 HC were included in this systematic review. The aMCI group showed significant gray matter atrophy in the left amygdala and right hippocampus, which was consistent with results from the ADNI dataset. Functional characterization revealed that these regions were mainly associated with emotion, cognition, and perception. Further, meta-regression analysis demonstrated that gray matter atrophy in the left inferior frontal gyrus and the left angular gyrus was significantly associated with cognitive impairment in the aMCI group. Conclusions: The findings of gray matter atrophy in the left amygdala and right hippocampus are highly consistent and robust, and not only offer a better understanding of the underlying neuropathology but also provide accurate potential biomarkers for aMCI.
Keywords: amnestic mild cognitive impairment; gray matter volume; meta-analysis; seed-based d mapping; voxel-based morphometry.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Liu, Lan, Huang, He, Yang, Li, Hu, Xu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

