Efficacy and Safety of Monoclonal Antibody Against Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide or Its Receptor for Migraine: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
- PMID: 33867991
- PMCID: PMC8045977
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.649143
Efficacy and Safety of Monoclonal Antibody Against Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide or Its Receptor for Migraine: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Abstract
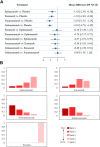
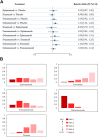
Background: The optimal monoclonal antibody against calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) for adult patients with migraine has yet to be determined. Therefore, we aimed to compare the effectiveness of different monoclonal antibodies against CGRP or its receptor for adult patients with migraine through a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Methods: We systematically searched the MEDILNE, Embase, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Cochrane Library databases for relevant publications from inception until October 30, 2020. Only randomized clinical trials of adults with migraine that assessed any calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody and reported clinical outcomes were included. The primary outcomes were changes in monthly migraine days and treatment-emergent adverse events Results: We initially retrieved 2,070 publications, and ultimately, 18 randomized clinical trials totaling 8,926 patients were included. In terms of efficacy, eptinezumab (MD -1.43, 95% CrI -2.59 to -0.36), erenumab (MD -1.61, 95% CrI -2.40 to -0.84), fremanezumab (MD -2.19, 95% CrI -3.15 to -1.25), and galcanezumab (MD -2.10, 95% CrI -2.76 to -1.45) significantly reduced MMDs compared with placebo. In terms of safety, only galcanezumab increased the incidences of TEAEs (RR 1.11, 95% CrI 1.01-1.22) and serious adverse events (RR 2.95, 95% CrI 1.41-6.87) compared with placebo. Conclusion: Most drugs performed similarly and were superior to placebo in most of our analyses. Further head-to-head research on different types of CGRP monoclonal antibodies is necessary to validate the present findings.
Keywords: calcitonin gene-related peptide; headache; meta-analysis; migraine; monoclonal antibody.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Chen, Song and You.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody against calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor for migraine patients with prior preventive treatment failure: a network meta-analysis.J Headache Pain. 2022 Sep 8;23(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s10194-022-01472-2. J Headache Pain. 2022. PMID: 36071388 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody for episodic migraine: a meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2018 Dec;39(12):2097-2106. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3547-3. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30182284
-
Indirect Comparison of Topiramate and Monoclonal Antibodies Against CGRP or Its Receptor for the Prophylaxis of Episodic Migraine: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.CNS Drugs. 2021 Aug;35(8):805-820. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00834-9. Epub 2021 Jul 16. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34272688 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and tolerability of calcitonin-gene-related peptide binding monoclonal antibodies for the prevention of episodic migraine - a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Cephalalgia. 2019 Aug;39(9):1164-1179. doi: 10.1177/0333102419829007. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Cephalalgia. 2019. PMID: 30789292
-
The Safety and Efficacy of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Monoclonal Antibodies for the Preventive Treatment of Migraine: A Protocol for Multiple-Treatment Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 3;19(3):1753. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031753. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35162776 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Higher Circulating Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With Decreased Migraine Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 8;9:907789. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.907789. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36159496 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical effectiveness of pharmacological interventions for managing chronic migraine in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Headache Pain. 2023 Dec 6;24(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01696-w. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 38057728 Free PMC article.
-
Why are CGRP monoclonal antibodies not yet the first line treatment in migraine prevention?Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022 May;80(5 Suppl 1):214-217. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X-ANP-2022-S125. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022. PMID: 35976315 Free PMC article.
-
Second messenger signalling bypasses CGRP receptor blockade to provoke migraine attacks in humans.Brain. 2023 Dec 1;146(12):5224-5234. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad261. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37540009 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Anti-calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Monoclonal Antibodies in Preventing Migraines: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 19;15(9):e45560. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45560. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37868560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashina M., Goadsby P. J., Reuter U., Silberstein S., Dodick D. W., Xue F., et al. (2021). Long-term efficacy and safety of erenumab in migraine prevention: results from a 5-year, open-label treatment phase of a randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Neurol. [Online ahead of print]. 10.1111/ene.14715 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bigal M. E., Dodick D. W., Rapoport A. M., Silberstein S. D., Ma Y., Yang R., et al. (2015). Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of TEV-48125 for preventive treatment of high-frequency episodic migraine: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b study. Lancet Neurol. 14, 1081–1090. 10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00249-5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

