Anosognosia in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Lack of Awareness of Memory Difficulties Characterizes Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33868048
- PMCID: PMC8044313
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.631518
Anosognosia in Mild Cognitive Impairment: Lack of Awareness of Memory Difficulties Characterizes Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
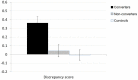
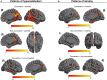
While anosognosia is often present in Alzheimer's disease, the degree of awareness of cognitive difficulties in the earlier stages, such as Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), is less clear. Using a questionnaire and Feeling-of-Knowing tasks, the aims of this study were (1) to test the hypothesis that anosognosia is present specifically in prodromal AD stage in patients that, owing to a more severe AD neuropathology, will rapidly progress to overt dementia and (2) to assess the neural bases of self-awareness for memory functioning. A group of 44 patients with amnestic MCI and a group of 29 healthy older participants (CTRL) performed two Feeling-of-Knowing tasks (episodic and semantic FOK) and responded to the Functional Memory Scale (MARS), also completed by one of their relatives. They underwent FDG-PET and structural MRI. The participants were followed clinically for 4 years. At the end of follow-up, 23 patients with MCI developed Alzheimer's disease (converters) and 21 patients still presented symptoms of MCI without progression (non-converters). The analyses focused on the data from inclusion stratified according to clinical status 4 years later (converters, non-converters, CTRL). On the episodic FOK task, converters patients overestimated their ability to later recognize unrecalled words and they showed prediction accuracy (Hamann coefficient) at the level of chance. No difficulty was observed in any group with the semantic FOK task. On the MARS, converters patients had a higher anosognosia score than non-converters patients and CTRL, which did not differ from each other. Correlations between self-awareness scores and neuroimaging data using small volume correction analyses in a priori regions of interest in converters indicated that inaccurate episodic FOK judgments was related to changes in brain areas that might support interpretation of retrieved content for judging the likelihood of recognition. For the MARS, the association between anosognosia and decreased gray matter density of the left inferior prefrontal cortex in converters might indicate poor inhibition over outdated personal knowledge. In amnestic MCI, anosognosia could be an early sign of neurodegeneration in brain areas that would support control mechanisms over memory representations.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; FDG-PET; MRI; Mild Cognitive Impairment; anosognosia; feeling-of-knowing; metamemory; self-awareness.
Copyright © 2021 Bastin, Giacomelli, Miévis, Lemaire, Guillaume and Salmon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Clare L, Wilson BA, Carter G, Roth I, Hodges JR. Assessing awareness in early-stage Alzheimer's disease: development and piloting of the Memory Awareness Rating Scale. Neuropsychol Rehabil. (2002) 12:341–62. 10.1080/09602010244000129 - DOI
-
- Ernst A, Moulin CJA, Souchay C, Mograbi DC, Morris R. Anosognosia and metacognition in Alzheimer's disease: insights from experimental psychology. In: Dunlosky J, Tauber SUK. editors. The Oxford Handbook of Metamemory. Oxford: Oxford University Press; (2015). pp. 451–72.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous