The Functional and Antiviral Activity of Interferon Alpha-Inducible IFI6 Against Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Gene Expression
- PMID: 33868257
- PMCID: PMC8047077
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.634937
The Functional and Antiviral Activity of Interferon Alpha-Inducible IFI6 Against Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Gene Expression
Abstract
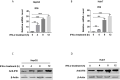
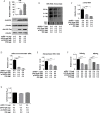
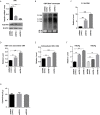
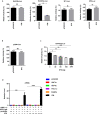
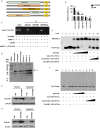
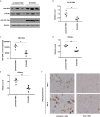
Hepatitis B virus is an enveloped DNA virus, that infects more than three hundred and sixty million people worldwide and leads to severe chronic liver diseases. Interferon-alpha inducible protein 6 (IFI6) is an IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) whose expression is highly regulated by the stimulation of type I IFN-alpha that restricts various kinds of virus infections by targeting different stages of the viral life cycle. This study aims to investigate the antiviral activity of IFI6 against HBV replication and gene expression. The IFI6 was highly induced by the stimulation of IFN-α in hepatoma cells. The overexpression of IFI6 inhibited while knockdown of IFI6 elevated replication and gene expression of HBV in HepG2 cells. Further study determined that IFI6 inhibited HBV replication by reducing EnhII/Cp of the HBV without affecting liver enriched transcription factors that have significant importance in regulating HBV enhancer activity. Furthermore, deletion mutation of EnhII/Cp and CHIP analysis revealed 100 bps (1715-1815 nt) putative sites involved in IFI6 mediated inhibition of HBV. Detailed analysis with EMSA demonstrated that 1715-1770 nt of EnhII/Cp was specifically involved in binding with IFI6 and restricted EnhII/Cp promoter activity. Moreover, IFI6 was localized mainly inside the nucleus to involve in the anti-HBV activity of IFI6. In vivo analysis based on the hydrodynamic injection of IFI6 expression plasmid along with HBV revealed significant inhibition of HBV DNA replication and gene expression. Overall, our results suggested a novel mechanism of IFI6 mediated HBV regulation that could develop potential therapeutics for efficient HBV infection treatment.
Keywords: CHIP; EMSA; HBV; IFI6; antiviral activity; interferon-stimulated genes.
Copyright © 2021 Sajid, Ullah, Yan, He, Feng, Shereen, Hao, Li, Guo, Chen and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SOX9 represses hepatitis B virus replication through binding to HBV EnhII/Cp and inhibiting the promoter activity.Antiviral Res. 2020 May;177:104761. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104761. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32147495
-
SOX2 Represses Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Binding to the Viral EnhII/Cp and Inhibiting the Promoter Activation.Viruses. 2020 Feb 29;12(3):273. doi: 10.3390/v12030273. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32121397 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activity of interferon-stimulated gene 20, as a putative repressor binding to hepatitis B virus enhancer II and core promoter.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Aug;35(8):1426-1436. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14986. Epub 2020 Feb 9. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31951295 Free PMC article.
-
Control of hepatitis B virus replication by interferons and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 7;20(33):11618-29. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11618. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25206268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus biology and life cycle.Antiviral Res. 2020 Oct;182:104925. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104925. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32866519 Review.
Cited by
-
Interferon and interferon-stimulated genes in HBV treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1034968. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1034968. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36531993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A machine learning model for predicting patients with major depressive disorder: A study based on transcriptomic data.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 8;16:949609. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.949609. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36003956 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological signatures unveiled by integrative systems vaccinology characterization of dengue vaccination trials and natural infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 20;15:1282754. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1282754. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38444851 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Host Restriction of Hepatitis B Virus Replication.Viruses. 2024 May 11;16(5):764. doi: 10.3390/v16050764. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IFN-stimulated gene IFI27 counteracts innate immune responses after viral infections by interfering with RIG-I signaling.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1176177. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1176177. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37187533 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

