MicroLet-7b Regulates Neutrophil Function and Dampens Neutrophilic Inflammation by Suppressing the Canonical TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 33868293
- PMCID: PMC8044834
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.653344
MicroLet-7b Regulates Neutrophil Function and Dampens Neutrophilic Inflammation by Suppressing the Canonical TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
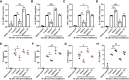
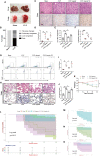
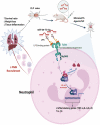
Sepsis is a heterogeneous syndrome caused by a dysregulated host response during the process of infection. Neutrophils are involved in the development of sepsis due to their essential role in host defense. COVID-19 is a viral sepsis. Disfunction of neutrophils in sepsis has been described in previous studies, however, little is known about the role of microRNA-let-7b (miR-let-7b), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity in neutrophils and how they participate in the development of sepsis. In this study, we investigated the regulatory pathway of miR-let-7b/TLR4/NF-κB in neutrophils. We also explored the downstream cytokines released by neutrophils following miR-let-7b treatment and its therapeutic effects in cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced septic mice. Six-to-eight-week-old male C57BL/6 mice underwent CLP following treatment with miR-let-7b agomir. Survival (n=10), changes in liver and lungs histopathology (n=4), circulating neutrophil counts (n=4), the liver-body weight ratio (n=4-7), and the lung wet-to-dry ratio (n=5-6) were recorded. We found that overexpression of miR-let-7b could significantly down-regulate the expression of human-derived neutrophilic TLR4 at a post-transcriptional level, a decreased level of proinflammatory factors including interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and an upregulation of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 in vitro. After miR-let-7b agomir treatment in vivo, neutrophil recruitment was inhibited and thus the injuries of liver and lungs in CLP-induced septic mice were alleviated (p=0.01 and p=0.04, respectively), less weight loss was reduced, and survival in septic mice was also significantly improved (p=0.013). Our study suggested that miR-let-7b could be a potential target of sepsis.
Keywords: COVID-19; MicroLet-7b; TLR4/NF-κB; inflammation; neutrophil; sepsis.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Han, Chen, Xie, Yang, Zhou, Zhang and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

