EZH2 Inhibition Interferes With the Activation of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Lupus Nephritis in NZB/NZW F1 Mice
- PMID: 33868295
- PMCID: PMC8044841
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.653989
EZH2 Inhibition Interferes With the Activation of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Lupus Nephritis in NZB/NZW F1 Mice
Abstract
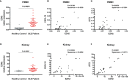
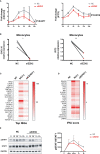
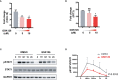
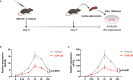
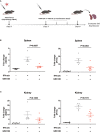
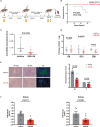
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is a histone-lysine N-methyltransferase mediating trimethylation of H3K27, which represses gene expression and is critical to immune regulation. Inhibition of EZH2 is proved to have the potential of treating many diseases. However, whether inhibition of EZH2 affects type I interferon (IFN-I) signaling pathway, the abnormality of which is an important pathogenic mechanism for SLE, is still elusive. Here, we report, unexpectedly, a positive regulatory function of EZH2 in IFN-I signaling pathway, which contributes to the overactivation of IFN-I signaling pathway in SLE. We show that the expression of EZH2 was upregulated and positively correlated with the overexpression of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs) in both peripheral blood mononuclear cells and renal tissues of SLE patients. In vitro inhibition of EZH2 by either siRNAs or chemical inhibitors reduced the phosphorylation of STAT1 and the induction of ISGs stimulated by IFN-I. Additionally, inhibition of EZH2 interfered with the in vivo and ex vivo activation of IFN-I signaling pathway elicited by intravenous injection of adenovirus vector expressing mouse IFN-α5 and exogeneous stimulation with IFN-α, respectively. We evaluated the therapeutic effects of EZH2 inhibitor in NZB/NZW F1 mice which depend on IFN-I signaling pathway for the lupus-like disease development. Administration of EZH2 inhibitor prolonged the survival, reduced the levels of anti-dsDNA autoantibodies, and improved lupus nephritis of the mice. What's more, EZH2 inhibitor attenuated the expression of ISGs in the kidneys of these mice. In summary, we show that excessive EZH2 contributes to the overactivation of IFN-I signaling pathway in SLE. EZH2 inhibitor has the potential to inhibit IFN-I signaling pathway and alleviate lupus nephritis. Additionally, diverse disease driving pathways exist among systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patient, and even in the same patients. Common regulators of different pathogenic pathways can be multivalent therapeutic targets. Together with previous studies showing EZH2 is involved in T-cell and B-cell mediated immune responses, EZH2 could be a potent multivalent therapeutic target for SLE.
Keywords: enhancer of zeste homolog 2; epigenetics; multivalent therapeutic target; systemic lupus erythematosus; type I interferon.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Jiang, Qi, Zhang, Qu and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 as a Novel Regulator of Type I Interferon Signaling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 May;68(5):1222-32. doi: 10.1002/art.39543. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26663909
-
Downregulation of Renal Hsa-miR-127-3p Contributes to the Overactivation of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway in the Kidney of Lupus Nephritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 21;12:747616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.747616. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34745118 Free PMC article.
-
Pim-1 as a Therapeutic Target in Lupus Nephritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Aug;71(8):1308-1318. doi: 10.1002/art.40863. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30791224
-
Therapeutically targeting proinflammatory type I interferons in systemic lupus erythematosus: efficacy and insufficiency with a specific focus on lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 16;15:1489205. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1489205. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39478861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormalities of the type I interferon signaling pathway in lupus autoimmunity.Cytokine. 2021 Oct;146:155633. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155633. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 34340046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ezh2 Knockout in B Cells Impairs Plasmablast Differentiation and Ameliorates Lupus-like Disease in MRL/lpr Mice.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 Aug;75(8):1395-1406. doi: 10.1002/art.42492. Epub 2023 May 31. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36897808 Free PMC article.
-
PRC2-Mediated Epigenetic Suppression of Type I IFN-STAT2 Signaling Impairs Antitumor Immunity in Luminal Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 16;82(24):4624-4640. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0736. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36222718 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of B cells and its role in autoimmune pathogenesis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2022 Nov;19(11):1215-1234. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00933-7. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36220996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decipher the Immunopathological Mechanisms and Set Up Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Patients with Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 13;24(12):10066. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210066. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2 Promotes T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation Through Enhancing STAT3 Phosphorylation in Patients With Primary Sjögren's Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 20;13:922871. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922871. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35795677 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

