LncRNAs: Architectural Scaffolds or More Potential Roles in Phase Separation
- PMID: 33868368
- PMCID: PMC8044363
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.626234
LncRNAs: Architectural Scaffolds or More Potential Roles in Phase Separation
Abstract
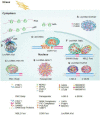
Biomolecules specifically aggregate in the cytoplasm and nucleus, driving liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) formation and diverse biological processes. Extensive studies have focused on revealing multiple functional membraneless organelles in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Condensation compositions of LLPS, such as proteins and RNAs affecting the formation of phase separation, have been gradually unveiled. LncRNAs possessing abundant second structures usually promote phase separation formation by providing architectural scaffolds for diverse RNAs and proteins interaction in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Beyond scaffolds, lncRNAs may possess more diverse functions, such as functioning as enhancer RNAs or buffers. In this review, we summarized current studies on the function of phase separation and its related lncRNAs, mainly in the nucleus. This review will facilitate our understanding of the formation and function of phase separation and the role of lncRNAs in these processes and related biological activities. A deeper understanding of the formation and maintaining of phase separation will be beneficial for disease diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: lncRNAs; nuclear bodies; phase separation; signaling transduction; therapeutics treatments.
Copyright © 2021 Luo, Qu, Gao, Lin, Liu and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aly M. K., Ninomiya K., Adachi S., Natsume T., Hirose T. (2019). Two distinct nuclear stress bodies containing different sets of RNA-binding proteins are formed with HSATIII architectural noncoding RNAs upon thermal stress exposure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 516 419–423. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.061 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

