A Mendelian Randomization Study of Plasma Homocysteine Levels and Cerebrovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 33868384
- PMCID: PMC8047106
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.653032
A Mendelian Randomization Study of Plasma Homocysteine Levels and Cerebrovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
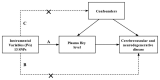
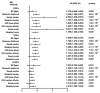
Background: Homocysteine (Hcy) is a toxic amino acid and hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) was reported to be associated with both cerebrovascular disease and neurodegenerative disease. Our aim was to assess the causal link between plasma Hcy level and cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases through a Mendelian randomization (MR) study. Methods: A two-sample MR study was performed to infer the causal link. We extracted the genetic variants (SNPs) associated with plasma Hcy level from a large genome-wide association study (GWAS) meta-analysis. The main MR analysis was performed using the inverse variance-weighted method. Additional analyses were further performed using MR-Egger intercept and Cochran's Q statistic to detect the heterogeneity or pleiotropy of our findings. Results: Thirteen Hcy-associated SNPs were selected as instrumental variables. The results showed evidence of a causal link between plasma Hcy level and ischemic stroke (IS) caused by small artery occlusion (SAS, OR = 1.329, 95% CI 1.047-1.612, p = 0.048). Meanwhile, there was no evidence of association between plasma Hcy level and other types of IS, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or neurodegenerative disease. The MR-Egger intercept test indicated no evidence of directional pleiotropy. Results of additional MR analysis indicated that blood pressure (BP) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) serve as influencers in the association. Conclusion: The MR study found a little causal link between plasma Hcy level and SAS. The link is likely to be influenced by other risk factors like BP and T2DM.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; blood pressure; cerebrovascular disease; diabetes mellitus; homocysteine; neurodegenerative disease; small artery occlusion.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Zhang, Li, Liu, Tong, Fang, Zhang, Song, Xia and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.The reviewer YP declared a past co-authorship with the authors HF, BS and YX to the handling editor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mendelian randomization study to investigate the causal relationship between plasma homocysteine and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.World J Emerg Med. 2023;14(5):367-371. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.078. World J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37908800 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of homocysteine on the risk of coronary artery diseases in individuals with diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Mar;58(3):301-307. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01608-3. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33113028 Free PMC article.
-
Appraising the Causal Association of Plasma Homocysteine Levels With Atrial Fibrillation Risk: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Genet. 2021 May 26;12:619536. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.619536. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34122499 Free PMC article.
-
No causal association between plasma homocysteine levels and atrial fibrillation: A Mendelian randomization study.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021 Feb 8;31(2):587-591. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.10.012. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 33250370
-
The causal role of homocysteine in multiple diseases: a systematic review of Mendelian randomization studies.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025 May 20;22(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12986-025-00933-0. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40394620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Palm Oil Derived Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction Attenuates Vascular Dementia in Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13531. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113531. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362316 Free PMC article.
-
Mendelian randomization study to investigate the causal relationship between plasma homocysteine and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.World J Emerg Med. 2023;14(5):367-371. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.078. World J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37908800 Free PMC article.
-
The causal effect of physical activity intensity on COVID-19 susceptibility, hospitalization, and severity: Evidence from a mendelian randomization study.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1089637. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1089637. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36969605 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Study on the Time in Range of Blood Glucose and Type 2 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 28;2022:2743679. doi: 10.1155/2022/2743679. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9856823. doi: 10.1155/2023/9856823. PMID: 35937384 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Homocysteine and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Outcome-Wide Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses and Mendelian Randomization Studies.Adv Nutr. 2025 Jun;16(6):100434. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100434. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40288491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams H. P., Bendixen B. H., Kappelle L. J., Biller J., Love B. B., Gordon D. L., et al. . (1993). Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24, 35–41. 10.1161/01.STR.24.1.35, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

