Excision repair cross-complementing group 2 upregulation is a potential predictive biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma recurrence
- PMID: 33868488
- PMCID: PMC8045162
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12711
Excision repair cross-complementing group 2 upregulation is a potential predictive biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma recurrence
Abstract
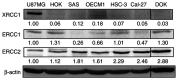
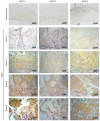
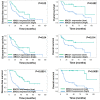
Oral cancer is the fourth most common type of cancer among males in Taiwan, and the prognosis for patients with advanced-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains poor. The present study investigated the prognostic value of three DNA repair genes, namely excision repair cross-complementing group 1 (ERCC1), ERCC2 and X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 (XRCC1) in OSCC. The protein expression levels of XRCC1, ERCC1 and ERCC2 in oral cell lines were analyzed via western blotting and immunohistochemistry using samples from 98 patients with biopsy-proven OSCC, while the χ2 test was used to analyze the clinicopathological association. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to determine the prognostic value of XRCC1, ERCC1 and ERCC2 for overall survival, and the log-rank test was used to evaluate the significance of differences. Multivariate analysis revealed a positive association between ERCC2 expression and OSCC recurrence (19.64-fold; 95% CI, 5.00-77.1; P<0.001). In addition, the high protein expression levels of XRCC1, ERCC1 and ERCC2 were associated with poor disease-free and overall survival rates. Therefore, the present study suggested that high ERCC2 expression may be a risk factor for OSCC recurrence.
Keywords: DNA repair; X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1; excision repair cross-complementing group 1; excision repair cross-complementing group 2; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright: © Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive Value of ERCC1, ERCC2, and XRCC Expression for Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Gastric Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant mFOLFOX-4 Chemotherapy.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Apr;26(2):1105-1116. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00666-5. Epub 2019 May 10. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31077069 Clinical Trial.
-
Decreased expression of DNA repair genes (XRCC1, ERCC1, ERCC2, and ERCC4) in squamous intraepithelial lesion and invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 May;377(1-2):45-53. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1569-y. Epub 2013 Feb 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23435956
-
Relationship Between Expression of Proteins ERCC1, ERCC2, and XRCC1 and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Rectal Cancer Treated with FOLFOX-Based Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy.World J Surg. 2017 Nov;41(11):2884-2897. doi: 10.1007/s00268-017-4070-z. World J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28608017
-
Predictive value of ERCC1, ERCC2, and XRCC1 overexpression for stage III colorectal cancer patients receiving FOLFOX-4 adjuvant chemotherapy.J Surg Oncol. 2013 Dec;108(7):457-64. doi: 10.1002/jso.23422. Epub 2013 Aug 31. J Surg Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23996617
-
The prognostic and predictive value of excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1) protein in 1288 patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with platinum-based therapy: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Sep;273(9):2305-17. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3710-x. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26179868 Review.
Cited by
-
A multimodal approach for establishing ACTL6A and ERCC1 as chemoresistance genes in locally advanced head and neck cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 29;16:1541987. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1541987. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40510426 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of XRCC1 is Associated with Poor Survival in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma and Has Potential to Be Used as Targeted Therapy by Synthetic Lethality.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Oct 1;24(10):3525-3535. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.10.3525. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37898859 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic signatures of ERCC1 and ERCC2 expression, along with SNPs variants, unveil favorable prognosis in SCLC patients undergoing platinum-based chemotherapy.Oncol Res. 2024 Dec 20;33(1):45-55. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.050161. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39735668 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Tobacco's Impact on DNA Repair Genes and Risks in Oral Precancer and Cancer: A Comprehensive Research Study.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2024 Aug;23(4):808-815. doi: 10.1007/s12663-024-02234-0. Epub 2024 Jun 15. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2024. PMID: 39118938 Free PMC article.
-
Survival association of XRCC1 for patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 5;13:1035910. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1035910. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36685969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ministry of Health Welfare, corp-author. The cause of death in Taiwan in 2018. https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=269&pid=13498
-
- Liao CT, Wang HM, Ng SH, Yen TC, Lee LY, Hsueh C, Wei FC, Chen IH, Kang CJ, Huang SF, Chang JT. Good tumor control and survivals of squamous cell carcinoma of buccal mucosa treated with radical surgery with or without neck dissection in Taiwan. Oral Oncol. 2006;42:800–809. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.11.020. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
