The effect of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields following on upregulation of miR-21 and miR-29 in gastric cancer cell line
- PMID: 33868612
- PMCID: PMC8035540
The effect of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields following on upregulation of miR-21 and miR-29 in gastric cancer cell line
Abstract
Aim: Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields affect miRNAs expression in cancer cell. In this study, electromagnetic fields exposed to low frequency were used to compare miR-21 and miR-29 expressions in a gastric cancer cell line.
Background: It has been recently suggested that the low frequency electromagnetic fields probably function as a treatment for cancers.
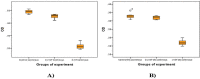
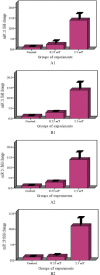
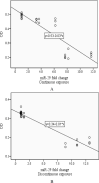
Methods: A cultured cell line of gastric cancer was exposed to an electromagnetic radiation system. The cell line was assigned to 4 groups under continuous and discontinuous radiations of 0.25 and 2.5 ml Tesla field strength. Then, the groups were compared with a non-radiation control group. Later, RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were prepared for miR-21 and miR-29. Real Time PCR method was used to determine how expressions of these two microRNAs differ. Finally, the results were statistically analyzed.
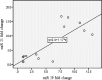
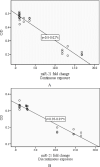
Results: The percentage of cell viability in the electromagnetic field radiation experienced a significant decrease compared to that of the control group. In addition, expression of miRNA-21 and miRNA-29 had a significant increase as the strength of the electromagnetic field radiations was on an upward trend. Similarly, the percentage of cell viability saw a significant decline in the upregulation of miRNA-21 and miRNA-29 regardless of radiation types.
Conclusion: Findings of this study showed the therapeutic effect of low frequency electromagnetic fields on the gastric cancer cell line. They also indicated that novel biomarkers (miRNA-21 and miRNA-29) could be proposed as potential treatments of gastric cancer, but the results are required to be well established by future studies.
Keywords: Electromagnetic field; Gastric cancer cell line; expression; miR-21; miR-29.
©2021 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EVALUATION OF BCL2 AND ITS REGULATORY MIRS, MIR-15-B AND MIR-16 EXPRESSION CHANGES UNDER THE EXPOSURE OF EXTREMELY LOW-FREQUENCY ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS ON HUMAN GASTRIC CANCER CELL LINE.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2021 Dec 17;197(2):93-100. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncab163. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2021. PMID: 34791478
-
Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields Affect the miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Signaling Pathways in the GC-2 Cell Line.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 6;10(10):e0139949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139949. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26439850 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of miR-144 and miR-375 in the human gastric cancer cell line following the exposure to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields.Int J Radiat Biol. 2021;97(9):1324-1332. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2021.1941376. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Int J Radiat Biol. 2021. PMID: 34125651
-
A systematic review of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer.Immunogenetics. 2021 Apr;73(2):155-161. doi: 10.1007/s00251-020-01201-6. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Immunogenetics. 2021. PMID: 33399935
-
Impact of Long-Lasting Environmental Factors on Regulation Mediated by the miR-34 Family.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 12;12(2):424. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020424. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Zarea K, Beiranvand S, Ghanbari S, Hanna Tuvesson H. Incidence of Gastrointestinal Cancers in Iran: A Systematic Review. Jundishapur J Chronic Dis Care. 2017;6:e37224.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
