Transcriptomic dynamics changes related to anthocyanin accumulation in the fleshy roots of carmine radish (Raphanus sativus L.) characterized using RNA-Seq
- PMID: 33868802
- PMCID: PMC8035900
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10978
Transcriptomic dynamics changes related to anthocyanin accumulation in the fleshy roots of carmine radish (Raphanus sativus L.) characterized using RNA-Seq
Abstract
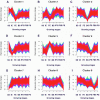
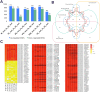
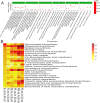
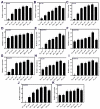
Carmine radish is famous for containing a natural red pigment (red radish pigment). However, the expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis-related genes during the dynamic development stages of the fleshy roots in carmine radish has not been fully investigated. Here, based on HPLC quantification of anthocyanin levels from our previous study, young fleshy roots of the carmine radish "Hongxin 1" obtained at the dynamic development stages of fleshy roots (seedling stage (SS), initial expansion (IE), full expansion (FE), bolting stage (BS), initial flowering stage (IFS), full bloom stage (FBS) and podding stage (PS)) were used for RNA-Seq. Approximately 126 comodulated DEGs related to anthocyanin biosynthesis (common DEGs in the dynamic growth stages of fleshy roots in carmine radish) were identified, from which most DEGs appeared to be likely to participate in anthocyanin biosynthesis, including two transcription factors, RsMYB and RsRZFP. In addition, some related proteins, e.g., RsCHS, RsDFR, RsANS, RsF'3H, RsF3GGT1, Rs3AT1, RsGSTF12, RsUFGT78D2 and RsUDGT-75C1, were found as candidate contributors to the regulatory mechanism of anthocyanin synthesis in the fleshy roots of carmine radish. In addition, 11 putative DEGs related to anthocyanin synthesis were evaluated by qRT-PCR via the (2-ΔΔCT) method; the Pearson correlation analysis indicated excellent concordance between the RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR results. Furthermore, GO enrichment analysis showed that "anthocyanin-containing compound biosynthetic process" and "anthocyanin-containing compound metabolic process" were commonly overrepresented in the dynamic growth stages of fleshy roots after the initial expansion stage. Moreover, five significantly enriched pathways were identified among the DEGs in the dynamic growth stages of fleshy roots in carmine radish, namely, flavonoid biosynthesis, flavone and flavonol biosynthesis, diterpenoid biosynthesis, anthocyanin biosynthesis, and benzoxazinoid biosynthesis. In conclusion, these results will expand our understanding of the complex molecular mechanisms of anthocyanin biosynthesis in the fleshy roots of carmine radish and the putative candidate genes involved in this process.
Keywords: Anthocyanin biosynthesis; Anthocyanins; Differential expression genes (DEGs); KEGG pathway enrichment; Radish (Raphanus sativus L.).
© 2021 Song et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aza-González C, Herrera-Isidrón L, Núñez-Palenius HG, Vega OMDL, Ochoa-Alejo N. Anthocyanin accumulation and expression analysis of biosynthesis-related genes during chili pepper fruit development. Biologia Plantarum. 2012;57(1):49–55. doi: 10.1007/s10535-012-0265-1. - DOI
-
- Azuma A. Genetic and environmental impacts on the biosynthesis of anthocyanins in grapes. Horticulture Journal. 2017;87(3):1–17.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

