The Biomarker Potential of Caveolin-1 in Penile Cancer
- PMID: 33868995
- PMCID: PMC8045968
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.606122
The Biomarker Potential of Caveolin-1 in Penile Cancer
Abstract
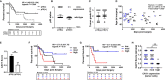
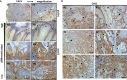
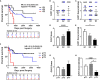
Various types of human cancers were characterized by an altered expression of epithelial or stromal caveolin-1 (CAV1). However, the clinical significance of CAV1 expression in penile cancer remains largely unknown. Here the expression patterns of CAV1 were analyzed in a retrospective cohort (n=43) of penile squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). Upon penile cancer progression, significantly increased CAV1-levels were determined within the malignant epithelium, whereas within the tumor stroma, namely the fibroblastic tumor compartment harboring activated and/or cancer associated fibroblasts, CAV1 levels significantly decline. Concerning the clinicopathological significance of CAV1 expression in penile cancer as well as respective epithelial-stromal CAV1 distributions, high expression within the tumor cells as well as low expression of CAV1 within the stromal compartment were correlated with decreased overall survival of penile cancer patients. Herein, CAV1 expressions and distributions at advanced penile cancer stages were independent of the immunohistochemically proven tumor protein p53 status. In contrast, less differentiated p16-positive tumor epithelia (indicative for human papilloma virus infection) were characterized by significantly decreased CAV1 levels. Conclusively, we provide further and new evidence that the characteristic shift in stromal-epithelial CAV1 being functionally relevant to tumor progression even occurs in penile SCC.
Keywords: biomarker; caveolin-1; microenvironment; p16; p53; penile cancer; tumor stroma.
Copyright © 2021 Panic, Reis, Wittka, Darr, Hadaschik, Jendrossek and Klein.
Conflict of interest statement
BH reports personal fees from ABX, Bayer, Lightpoint Medical, Inc., Janssen R&D, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, and Astellas, and travel from AstraZeneca, Janssen R&D, and Astellas. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stromal Caveolin-1 and Caveolin-2 Expression in Primary Tumors and Lymph Node Metastases.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018 Apr 10;2018:8651790. doi: 10.1155/2018/8651790. eCollection 2018. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018. PMID: 29850392 Free PMC article.
-
Progression-related loss of stromal Caveolin 1 levels fosters the growth of human PC3 xenografts and mediates radiation resistance.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 23;7:41138. doi: 10.1038/srep41138. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28112237 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal Fibroblasts Counteract the Caveolin-1-Dependent Radiation Response of LNCaP Prostate Carcinoma Cells.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 26;12:802482. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.802482. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35155239 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance and therapeutic implications of Caveolin-1 in gastrointestinal tract malignancies.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 May;233:108028. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.108028. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34755606 Review.
-
Caveolin-1, cancer and therapy resistance.Int J Cancer. 2018 Nov 1;143(9):2092-2104. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31369. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29524224 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Novel Biomarkers in Penile Carcinoma: A Prospective Review.J Pers Med. 2022 Aug 24;12(9):1364. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091364. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1 and the Deubiquitinase USP9x Are Cooperatively Upregulated during Prostate Cancer Progression and Limit Response of Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 26;15(9):2496. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092496. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173959 Free PMC article.
-
miR-138-5p-mediated HOXD11 promotes cell invasion and metastasis by activating the FN1/MMP2/MMP9 pathway and predicts poor prognosis in penile squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 23;13(9):816. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05261-2. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36151071 Free PMC article.
-
HPV and Penile Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Clinical Insights.Pathogens. 2024 Sep 18;13(9):809. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090809. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39339000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Location May Independently Predict Survival in Patients With M0 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Penis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 5;12:927088. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927088. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35865480 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

