Downregulation of hsa_circ_0001836 Induces Pyroptosis Cell Death in Glioma Cells via Epigenetically Upregulating NLRP1
- PMID: 33869006
- PMCID: PMC8044449
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.622727
Downregulation of hsa_circ_0001836 Induces Pyroptosis Cell Death in Glioma Cells via Epigenetically Upregulating NLRP1
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Downregulation of hsa_circ_0001836 Induces Pyroptosis Cell Death in Glioma Cells via Epigenetically Upregulating NLRP1.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 29;11:840877. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.840877. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35036362 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: It has been shown that circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a vital role in the progression of glioma. Recently, hsa_circ_0001836 was found to be upregulated in glioma tissues, but the role of hsa_circ_0001836 in glioma remains unclear.
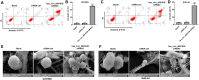
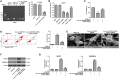
Methods: EdU staining and flow cytometry assays were used to measure the viability and death of glioma cells. In addition, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the morphology of cells undergoing cell death.
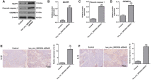
Results: Hsa_circ_0001836 expression was upregulated in U251MG and SHG-44 cells. In addition, hsa_circ_0001836 knockdown significantly reduced the viability and proliferation of U251MG and SHG-44 cells. Moreover, hsa_circ_0001836 knockdown markedly induced the pyroptosis of U251MG and SHG-44 cells, evidenced by the increased expressions of NLRP1, cleaved caspase 1 and GSDMD-N. Meanwhile, methylation specific PCR (MSP) results indicated that hsa_circ_0001836 knockdown epigenetically increased NLRP1 expression via mediating DNA demethylation of NLRP1 promoter region. Furthermore, downregulation of hsa_circ_0001836 notably induced pyroptosis and inhibited tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model of glioma.
Conclusion: Collectively, hsa_circ_0001836 knockdown could induce pyroptosis cell death in glioma cells in vitro and in vivo via epigenetically upregulating NLRP1 expression. These findings suggested that hsa_circ_0001836 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of glioma.
Keywords: NLRP1; circular RNA; glioma; methylation; pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Wu, Jing, Li, Dong and Meng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

