B7 Family Members in Lymphoma: Promising Novel Targets for Tumor Immunotherapy?
- PMID: 33869045
- PMCID: PMC8044412
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.647526
B7 Family Members in Lymphoma: Promising Novel Targets for Tumor Immunotherapy?
Abstract
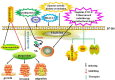
T cells play a vital role in the immune responses against tumors. Costimulatory or coinhibitory molecules regulate T cell activation. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) have shown remarkable benefits in patients with various tumor, but few patients have displayed significant immune responses against tumors after PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy and many have been completely unresponsive. Thus, researchers must explore novel immune checkpoints that trigger durable antitumor responses and improve clinical outcomes. In this regard, other B7 family checkpoint molecules have been identified, namely PD-L2, B7-H2, B7-H3, B7-H4 and B7-H6. The aim of the present article was to address the expression, clinical significance and roles of B7 family molecules in lymphoma, as well as in T and NK cell-mediated tumor immunity. B7 family checkpoints may offer novel and immunotherapeutic strategies for patients with lymphoma.
Keywords: B7-H2; B7-H3; B7-H4; B7-H6; PD-L1; PD-L2; lymphoma.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Qiu, Xie, Fu, Wang and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

