Salivary Microbiome Variation in Early Childhood Caries of Children 3-6 Years of Age and Its Association With Iron Deficiency Anemia and Extrinsic Black Stain
- PMID: 33869076
- PMCID: PMC8044945
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.628327
Salivary Microbiome Variation in Early Childhood Caries of Children 3-6 Years of Age and Its Association With Iron Deficiency Anemia and Extrinsic Black Stain
Abstract
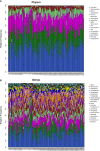
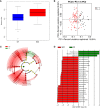
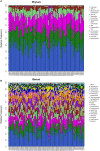
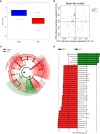
ECC is a common clinical manifestation of the oral cavity in childhood and Iron deficiency-anemia (IDA) is a high-risk factor but extrinsic black stain on the tooth surface is a protective factor for caries. There is limited information about oral microecological change in early children who suffer from ECC with IDA and extrinsic black stain (BS). This study enrolled 136 children aged 3-6 years. Dental caries and teeth BS were examined. Saliva was collected for 16S rRNA gene and fingertip blood were for Hemoglobin test. There are 93 ECC including 13 with IDA (IDA ECC) and 80 without IDA (NIDA ECC) and 43 caries free (CF) including 17 with BS (BSCF) and 26 without BS (NBS CF). Statistical analysis of microbiota data showed differences of the oral flora in different groups. The oral flora of the IDA ECC group had a high diversity, while the BSCF group had a low diversity. The bacterial genera Bacillus, Moraxella, and Rhodococcus were enriched in the IDA ECC while Neisseria was enriched in the NIDA ECC. Neisseria only exhibited high abundance in the BSCF, and the remaining genera exhibited high abundance in the NBSCF. Interestingly, the BSCF had the same trend as the NIDA ECC, and the opposite trend was observed with IDA ECC. We established random forest classifier using these biomarkers to predict disease outcomes. The random forest classifier achieved the best accuracy in predicting the outcome of caries, anemia and black stain using seven, one and eight biomarkers, respectively; and the accuracies of the classifiers were 93.35%, 94.62% and 95.23%, respectively. Our selected biomarkers can achieve good prediction, suggesting their potential clinical implications.
Keywords: children 3-6 years of age; early childhood caries (ECC); extrinsic black stain (BS); iron deficiency anemia (IDA); salivary microbiome variation.
Copyright © 2021 Han, Yue, Lin, Du, Wang, Wang, Kong, Wang, Gao, Ma and Bu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- (2016. b). Policy on Early Childhood Caries (ECC): Classifications, Consequences, and Preventive Strategies. Pediatr. Dent. 38 (6), 52–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

