Successful Use of a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist as Add-on Therapy to Sulfonylurea in the Treatment of KCNJ11 Neonatal Diabetes
- PMID: 33869096
- PMCID: PMC8046272
- DOI: 10.12890/2021_002352
Successful Use of a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist as Add-on Therapy to Sulfonylurea in the Treatment of KCNJ11 Neonatal Diabetes
Abstract
Sulfonylurea monotherapy is the standard treatment for patients with the most common form of permanent neonatal diabetes, KCNJ11 neonatal diabetes, but it is not always sufficient. For the first time, we present a case of successful use of a GLP-1 receptor agonist as add-on therapy in the treatment of a patient with KCNJ11 neonatal diabetes and insufficient effect of sulfonylurea monotherapy. Good glycaemic control was maintained with a HbA1c level of 48 mmol/mol (6.5%) at the end of 26 months' follow-up.
Learning points: Genetic testing is important in patients with neonatal diabetes.Sulfonylurea is the standard treatment for patients with the most common mutation (KCNJ11).We present the novel use of a GLP-1 receptor agonist as effective add-on therapy in a patient with KCNJ11 neonatal diabetes and insufficient effect of sulfonylurea monotherapy.
Keywords: GLP-1; KCNJ11; Neonatal diabetes; sulfonylurea.
© EFIM 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The authors did not receive funding for this work. MSS has received funding from the Danish Diabetes Academy for research not related to this work. SM has received research funding from Novo Nordisk and Boehringer-Ingelheim and honoraria from AstraZeneca, MSD, Sanofi and Novo Nordisk for research activities not related to this work.
Figures
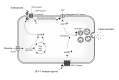

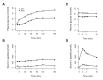
References
-
- Gade-Rasmussen B, Madsbad S, Svane MS, Martinussen C, Hansen T. [Successful treatment of KCNJ11 neonatal diabetes without insulin]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2018;180(46):V08180547. - PubMed
-
- Sastre J, Luque A, del Val F, Aragonés A, López J. Long-term efficacy of glibenclamide and sitagliptin therapy in adult patients with KCNJ11 permanent diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(3):e55–56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
