Ferroptosis Is a Potential Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target for Patients With Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 33869204
- PMCID: PMC8047193
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.649045
Ferroptosis Is a Potential Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target for Patients With Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Cardiomyocyte death is a fundamental progress in cardiomyopathy. However, the mechanism of triggering the death of myocardial cells remains unclear. Ferroptosis, which is the nonapoptotic, iron-dependent, and peroxidation-driven programmed cell death pathway, that is abundant and readily accessible, was not discovered until recently with a pharmacological approach. New researches have demonstrated the close relationship between ferroptosis and the development of many cardiovascular diseases, and several ferroptosis inhibitors, iron chelators, and small antioxidant molecules can relieve myocardial injury by blocking the ferroptosis pathways. Notably, ferroptosis is gradually being considered as an important cell death mechanism in the animal models with multiple cardiomyopathies. In this review, we will discuss the mechanism of ferroptosis and the important role of ferroptosis in cardiomyopathy with a special emphasis on the value of ferroptosis as a potential novel diagnostic and therapeutic target for patients suffering from cardiomyopathy in the future.
Keywords: cardiac damage; cardiomyopathy; ferroptosis; heart failure; regulated necrosis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhai, Zou, Liu, Xia and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
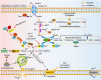
Similar articles
-
Targeting Ferroptosis to Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: A New Continent to Be Explored.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 30;9:737971. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.737971. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34527678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Feb 12;116(7):2672-2680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821022116. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30692261 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis and its role in cardiomyopathy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113279. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113279. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35738177 Review.
-
Targeting ferroptosis as a promising therapeutic strategy to treat cardiomyopathy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 13;14:1146651. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1146651. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37138856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(7):3052-3059. doi: 10.7150/thno.54113. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537073 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic cardioprotective effects of melatonin and deferoxamine through the improvement of ferritinophagy in doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 30;13:1050598. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1050598. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36531171 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Flavonoids in the Treatment of Iron Overload.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 5;9:685364. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.685364. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34291050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular and metabolic landscape of ferroptosis in respiratory diseases: Pharmacological aspects.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Jan;15(1):101050. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101050. Epub 2024 Jul 24. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40034685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relevance of Ferroptosis to Cardiotoxicity Caused by Anthracyclines: Mechanisms to Target Treatments.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 13;9:896792. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.896792. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35770215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Robust Rank Aggregation and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator Analysis of Novel Gene Signatures in Dilated Cardiomyopathy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 14;8:747803. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.747803. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34970603 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

