Iguratimod promotes transformation of mononuclear macrophages in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis by nuclear factor-κB pathway
- PMID: 33869594
- PMCID: PMC8026846
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2181
Iguratimod promotes transformation of mononuclear macrophages in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis by nuclear factor-κB pathway
Abstract
Background: The role of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its mechanism have attracted much attention in RA pathogenesis. Macrophages accumulate in the synoviums of RA, and the proportion of M1 type pro-inflammatory macrophages is higher than that of M2 type anti-inflammatory macrophages, leading to the secretion of inflammatory molecules and the aggravation of inflammatory reaction, which has made macrophages a potential target of RA drugs. Iguratimod is a kind of cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor that affects macrophage polarity. It is speculated that its anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic effects may be related to the regulation of macrophage M1/M2 ratio.
Aim: To investigate the effects of Iguratimod on the polarity of mononuclear macrophages in elderly patients with RA.
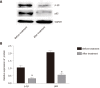
Methods: Elderly patients with RA and joint effusion were selected, including 10 men and 25 women, with an average age of 66.37 ± 4.42 years. Patients were treated with oral administration of 25 mg Iguratimod (Iremod, State Food and Drug Administration Approval No. H20110084) twice daily for 12 wk. Disease Activity Score 28 and Health Assessment Questionnaire score were collected according to the disease severity before and after treatment. Venous blood and joint effusion fluid were collected, mononuclear macrophages were extracted and expression of cell surface markers CD86, CD64, CD163, and CD206 was analyzed by flow cytometry. The concentration of inflammatory factors interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, transforming growth factor-β, and IL-4 in the joint effusion fluid was analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Expression of mononuclear cells inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (IκB) and phosphorylated IκB in peripheral blood was analyzed by western blotting.
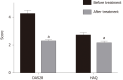
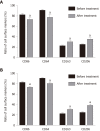
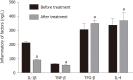
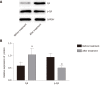
Results: Disease Activity Score 28 score and Health Assessment Questionnaire score of patients treated with Iguratimod decreased significantly. The percentage of cell surface markers CD86 and CD64 decreased significantly, and the percentage of CD163 and CD206 increased significantly (P < 0.05). The inflammatory factors IL-6 and IL-1β decreased significantly, and transforming growth factor-β and IL-4 increased significantly. Western blot analysis showed that mononuclear cell inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB in peripheral blood was significantly increased after treatment, and its phosphorylation level was significantly decreased (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Iguratimod can promote the transformation of mononuclear macrophages from M1 to M2 in elderly patients with RA by inhibiting the nuclear factor-κB pathway, thus improving symptoms of RA.
Keywords: Iguratimod; Macrophage; Nuclear factor-κB; Polarity; Rheumatoid arthritis.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TLR2 stimulation impairs anti-inflammatory activity of M2-like macrophages, generating a chimeric M1/M2 phenotype.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;19(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1447-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096690 Free PMC article.
-
CTLA4-Ig treatment induces M1-M2 shift in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Dec 24;23(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02691-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34952630 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 19;13:867260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867260. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35663975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of iguratimod and methotrexate on RANKL and OPG expression in serum and IL-1β-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Oct 31;62(12):44-50. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2016.62.12.8. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016. PMID: 27894399
-
Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review.Autoimmun Rev. 2019 Nov;18(11):102397. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102397. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Autoimmun Rev. 2019. PMID: 31520798
Cited by
-
Unveiling research hotspots: a bibliometric study on macrophages in musculoskeletal diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1519321. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1519321. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40356917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global scientific trends update on macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis: A bibliometric and visualized analysis from 2000 to 2022.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 9;9(9):e19761. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19761. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the molecular mechanism of iguratimod act on SLE using network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis.Front Bioinform. 2022 Sep 13;2:932114. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2022.932114. eCollection 2022. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36304300 Free PMC article.
-
[Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Dec 18;55(6):1013-1021. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.009. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 38101782 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Abeles AM, Pillinger MH. The role of the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: cartilage destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2006;64:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Cascão R, Rosário HS, Souto-Carneiro MM, Fonseca JE. Neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis: More than simple final effectors. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9:531–535. - PubMed
-
- Andreakos ET, Foxwell BM, Brennan FM, Maini RN, Feldmann M. Cytokines and anti-cytokine biologicals in autoimmunity: present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:299–313. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

