lncRNA MIR503HG inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in TNBC cells via the miR-224-5p/HOXA9 axis
- PMID: 33869743
- PMCID: PMC8027537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.03.009
lncRNA MIR503HG inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in TNBC cells via the miR-224-5p/HOXA9 axis
Abstract
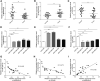
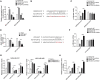
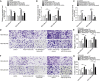
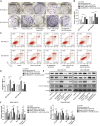
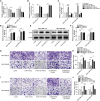
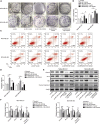
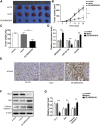
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly invasive subtype of breast cancer. This study investigated the molecular mechanism and influences of MIR503HG, miR-224-5p, and homeobox A9 (HOXA9) on TNBC cell growth and migration. Dual-luciferase reporter gene and RNA immunoprecipitation were performed to examine the regulation of MIR503HG, miR-224-5p, and HOXA9. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were evaluated by colony formation, flow cytometry, and Transwell assays. Finally, nude mice were employed to investigate the influence of MIR503HG on TNBC tumor growth. HOXA9 protein levels were detected by immunohistochemical staining. MIR503HG and HOXA9 expression were reduced in TNBC, while miR-224-5p was increased. Overexpression of MIR503HG or HOXA9 reduced the cell migration ability and proliferation and promoted apoptosis, and knockdown of MIR503HG or overexpression of miR-224-5p exhibited the opposite effects. Furthermore, MIR503HG promoted HOXA9 expression by inhibiting miR-224-5p. Overexpression of miR-224-5p reversed the effects of MIR503HG overexpression on TNBC cells, while overexpression of HOXA9 reversed the effect of MIR503HG knockdown. Additionally, an in vivo study proved that MIR503HG inhibited TNBC tumor growth via the miR-224-5p/HOXA9 axis. MIR503HG inhibited cell proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of TNBC cells via the miR-224-5p/HOXA9 axis, which may function as a novel target for the treatment of TNBC.
Keywords: HOXA9; MIR503HG; TNBC; lncRNA; miR-224-5p; triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shilpi S., Shivvedi R., Khatri K. Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Challenge for Current Cancer Therapy. J. Hum. Virol. Retrovirol. 2018;6:00189.
-
- da Silva J.L., Cardoso Nunes N.C., Izetti P., de Mesquita G.G., de Melo A.C. Triple negative breast cancer: A thorough review of biomarkers. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020;145:102855. - PubMed
-
- De Laurentiis M., Cianniello D., Caputo R., Stanzione B., Arpino G., Cinieri S., Lorusso V., De Placido S. Treatment of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): current options and future perspectives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2010;36(Suppl 3):S80–S86. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q., Gao S., Li H., Lv M., Lu C. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in triple negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017;232:3226–3233. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

