An Active Steering Hand-held Robotic System for Minimally Invasive Orthopaedic Surgery Using a Continuum Manipulator
- PMID: 33869745
- PMCID: PMC8052093
- DOI: 10.1109/lra.2021.3059634
An Active Steering Hand-held Robotic System for Minimally Invasive Orthopaedic Surgery Using a Continuum Manipulator
Abstract
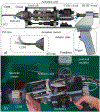
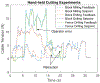
This paper presents the development and experimental evaluation of an active steering hand-held robotic system for milling and curved drilling in minimally invasive orthopaedic interventions. The system comprises a cable-driven continuum dexterous manipulator (CDM), an actuation unit with a handpiece, and a flexible, rotary cutting tool. Compared to conventional rigid drills, the proposed system enhances dexterity and reach in confined spaces in surgery, while providing direct control to the surgeon with sufficient stability while cutting/milling hard tissue. Of note, for cases that require precise motion, the system is able to be mounted on a positioning robot for additional controllability. A proportional-derivative (PD) controller for regulating drive cable tension is proposed for the stable steering of the CDM during cutting operations. The robotic system is characterized and tested with various tool rotational speeds and cable tensions, demonstrating successful cutting of three-dimensional and curvilinear tool paths in simulated cancellous bone and bone phantom. Material removal rates (MRRs) of up to 571 mm3/s are achieved for stable cutting, demonstrating great improvement over previous related works.
Keywords: Compliant Joints and Mechanisms; Medical Robots and Systems.
Figures





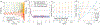
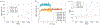
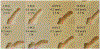

References
-
- Alambeigi F, Sefati S, Murphy RJ, Iordachita I and Armand M, ”Design and characterization of a debriding tool in robot-assisted treatment of osteolysis,” 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, 2016, pp. 5664–5669, doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2016.7487787. - DOI
-
- Murphy RJ, Kutzer MDM, Segreti SM, Lucas BC, and Armand M, ”Design and kinematic characterization of a surgical manipulator with a focus on treating osteolysis,” Robotica, vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 835–850, 2014. doi: 10.1017/S0263574713001082 - DOI
-
- Alambeigi F et al. , ”A Curved-Drilling Approach in Core Decompression of the Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Using a Continuum Manipulator,” in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 1480–1487, July 2017, doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2668469. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
