Primary evisceration for neonatal endogenous endophthalmitis: A report of two cases
- PMID: 33869894
- PMCID: PMC8042423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2021.101081
Primary evisceration for neonatal endogenous endophthalmitis: A report of two cases
Abstract
Purpose: To present two cases of neonatal endophthalmitis with poor prognosis that were managed with primary evisceration.
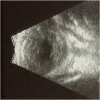
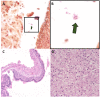
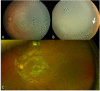
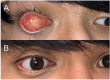
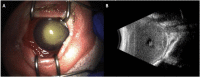
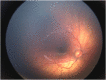
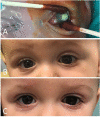
Observations: Case 1 is a 27-weeks' gestation neonate who developed Pseudomonas aeruginosa endophthalmitis complicated by globe rupture. Case 2 describes a 34-weeks' gestation neonate with Serratia marcescens endophthalmitis. Both patients had poor prognosis and thus underwent primary evisceration with good long-term cosmetic outcomes at 15 years and 17 months, respectively.
Conclusions and importance: Primary evisceration should be considered in neonates with endophthalmitis with a poor prognosis and can result in good long-term cosmesis.
Keywords: Endophthalmitis; Evisceration; Oculoplastics; Retina.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial disclosures to report.
Figures
References
-
- Jalali S., Pehere N., Rani P.K. Treatment outcomes and clinicomicrobiological characteristics of a protocol-based approach for neonatal endogenous endophthalmitis. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2014;24:424–436. - PubMed
-
- Jackson T.L., Eykyn S.J., Graham E.M., Stanford M.R. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: a 17-year prospective series and review of 267 reported cases. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003;48:403–423. - PubMed
-
- Stensvold H.J., Klingenberg C., Stoen R. Neonatal morbidity and 1-year survival of extremely preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2017;139 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

