Generating and capitalizing on the demographic dividend potential in sub-Saharan Africa: a conceptual framework from a systematic literature review
- PMID: 33870102
- PMCID: PMC8028847
- DOI: 10.12688/gatesopenres.13176.1
Generating and capitalizing on the demographic dividend potential in sub-Saharan Africa: a conceptual framework from a systematic literature review
Abstract
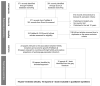
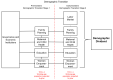
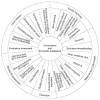
Background: Africa will double its population by 2050 and more than half will be below age 25. The continent has a unique opportunity to boost its socioeconomic welfare. This systematic literature review aims to develop a conceptual framework that identifies policies and programs that have provided a favorable environment for generating and harnessing a demographic dividend. This framework can facilitate sub-Saharan African countries' understanding of needed actions to accelerate their demographic transition and capitalize on their demographic dividend potential. Methods: The search strategy was structured around three concepts: economic development, fertility, and sub-Saharan Africa. Databases used included PubMed and EconLit. An inductive approach was employed to expand the reference base further. Data were extracted using literature records following a checklist of items to include when reporting a systematic review suggested in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement. Results: The final review consisted of 78 peer-reviewed articles, ten reports from the gray literature, and one book. Data were categorized according to relevant demographic dividend typology: pre-dividend and early-dividend. The results from the literature review were synthesized into a framework consisting of five sectors for pre-dividend countries, namely 1) Governance and Economic Institutions, 2) Family Planning, 3) Maternal and Child Health, 4) Education, and 5) Women's Empowerment. An additional sector, 6) Labor Market, is added for early-dividend countries. These sectors must work together to attain a demographic dividend. Conclusions: A country's demographic transition stage must guide policy and programs. Most sub-Saharan African countries have prioritized job creation and employment for youth, yet their efforts to secure a productive labor market require preliminary and complementary investments in governance, family planning, maternal and child health, education, and women's empowerment. Creating a favorable policy environment for generating and capitalizing on a demographic dividend can support their stated goals for development.
Keywords: demographic dividend; demographic transition; economic growth; fertility decline; sub-Saharan Africa.
Copyright: © 2020 Cardona C et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- African Union Commission: AU Roadmap on Harnessing the Demographic Dividend through Investments in Youth.2017a. Reference Source
-
- African Union Commission: Harnessing the demographic dividend through investment in youth.2017b. Reference Source
-
- Ahmed SA, Cruz M: Making the Most of Demographic Change in Southern Africa. The World Bank.2016. Reference Source
-
- Ahmed SA, Cruz M, Go DS, et al. : How Significant is Africa's Demographic Dividend for its Future Growth and Poverty Reduction? The World Bank.2014. Reference Source
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources