Serological investigation of asymptomatic cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals weak and declining antibody responses
- PMID: 33870851
- PMCID: PMC8143642
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1919032
Serological investigation of asymptomatic cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals weak and declining antibody responses
Abstract
Without an effective vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, the build-up of herd immunity through natural infection has been suggested as a means to control COVID-19. Although population immunity is typically estimated by the serological investigation of recovered patients, humoral immunity in asymptomatic subjects has not been well studied, although they represent a large proportion of all SARS-CoV-2 infection cases. In this study, we conducted a serosurvey of asymptomatic infections among food workers and performed serological and cellular response analyses of asymptomatic subjects in Wuhan, the original epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak. Our data showed that up to 5.91% of the food workers carried SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies asymptomatically; however, in 90.4% of them, the antibody level declined over a 2-week period. IgM and IgG antibodies, including neutralizing antibodies, were significantly lower in asymptomatic subjects than in recovered symptomatic patients with similar disease courses. Furthermore, the asymptomatic subjects showed lymphopenia and a prominent decrease in the B-cell population, as well as a low frequency of antibody-secreting cells and a low cytokine response. These factors probably contributed to the low and unsustained antibody levels in asymptomatic subjects. Our results show that asymptomatic subjects are likely to be vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2 reinfection, and neither the proportion of population immunity nor the breadth of immune responses is sufficient for herd immunity.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; asymptomatic; serology; weak antibody response.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
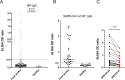
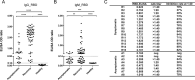
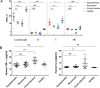
Similar articles
-
[Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM antibodies in Borgosesia (Piedmont Region, Northern Italy) population: a surveillance strategy in post-lockdown period?].Epidemiol Prev. 2020 Sep-Dec;44(5-6 Suppl 2):200-206. doi: 10.19191/EP20.5-6.S2.119. Epidemiol Prev. 2020. PMID: 33412811 Italian.
-
Antibody response using six different serological assays in a completely PCR-tested community after a coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak-the CoNAN study.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Mar;27(3):470.e1-470.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.11.009. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33221432 Free PMC article.
-
Highlighted Prospects of an IgM/IgG Antibodies Test in Identifying Individuals With Asymptomatic Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021 Jan 1;145(1):39-45. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2020-0310-SA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021. PMID: 32966561
-
A comparative review of immunoassays for COVID-19 detection.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Jun;17(6):573-599. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1908886. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33787412 Review.
-
Ravaging SARS-CoV-2: rudimentary diagnosis and puzzling immunological responses.Curr Med Res Opin. 2021 Feb;37(2):207-217. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2020.1862532. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Curr Med Res Opin. 2021. PMID: 33306409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetics of humoral immune response in patients with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19: a longitudinal study based in an in-house indirect ELISA method.EXCLI J. 2022 Aug 26;21:1167-1170. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-5337. eCollection 2022. EXCLI J. 2022. PMID: 36381645 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
What we know and still ignore on COVID-19 immune pathogenesis and a proposal based on the experience of allergic disorders.Allergy. 2022 Apr;77(4):1114-1128. doi: 10.1111/all.15112. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Allergy. 2022. PMID: 34582050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling SARS-CoV-2 propagation using rat coronavirus-associated shedding and transmission.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 23;16(11):e0260038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260038. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34813610 Free PMC article.
-
Under-diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infections among children aged 0-15 years, a nationwide seroprevalence study, Israel, January 2020 to March 2021.Euro Surveill. 2021 Dec;26(48):2101040. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.48.2101040. Euro Surveill. 2021. PMID: 34857069 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, robust, and sustainable antibody responses to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in convalescent COVID-19 individuals.JCI Insight. 2021 Oct 22;6(20):e151477. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.151477. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34499052 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
