Comparative analysis of three point-of-care lateral flow immunoassays for detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: data from 100 healthcare workers in Brazil
- PMID: 33871824
- PMCID: PMC8053894
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-021-00498-z
Comparative analysis of three point-of-care lateral flow immunoassays for detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: data from 100 healthcare workers in Brazil
Abstract
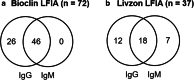
Since the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, Brazil has the third-highest number of confirmed cases and the second-highest number of recovered patients. SARS-CoV-2 detection by real-time RT-PCR is the gold standard but requires a certified laboratory infrastructure with high-cost equipment and trained personnel. However, for large-scale testing, diagnostics should be fast, cost-effective, widely available, and deployed for the community, such as serological tests based on lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) for IgM/IgG detection. We evaluated three different commercial point-of-care (POC) LFIAs for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG detection in capillary whole blood of 100 healthcare workers (HCW) from São Paulo university hospital previously tested by RT-PCR: (1) COVID-19 IgG/IgM BIO (Bioclin, Brazil), (2) Diagnostic Kit for IgM/IgG Antibody to Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) (Livzon, China), and (3) SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test (Wondfo, China). A total of 84 positives and 16 negatives HCW were tested. The data was also analyzed by the number of days post symptoms (DPS) in three groups: <30 (n=26), 30-59 (n=42), and >59 (n=16). The observed sensibility was 85.71%, 47.62%, and 44.05% for Bioclin, Wondfo, and Livzon, respectively, with a specificity of 100% for all LFIA. Bioclin was more sensitive (p<0.01), regardless of the DPS. Thus, the Bioclin may be used as a POC test to monitor SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in HCW.
Keywords: COVID-19; Healthcare workers; Lateral flow immunoassay; Point-of-care; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021. Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Situation Report –51 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/.
-
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological update - 2 February 2021: World Health Organization; 2021 [cited 2021 February 09]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update%2D....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous