Heat-inactivated Lactobacillus plantarum nF1 promotes intestinal health in Loperamide-induced constipation rats
- PMID: 33872333
- PMCID: PMC8055018
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250354
Heat-inactivated Lactobacillus plantarum nF1 promotes intestinal health in Loperamide-induced constipation rats
Abstract
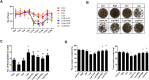
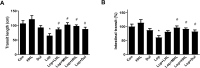
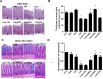
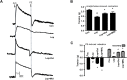
Constipation is a common condition that affects individuals of all ages, and prolonged constipation needs to be prevented to avoid potential complications and reduce the additional stress on individuals with pre-medical conditions. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of heat-inactivated Lactobacillus plantarum (HLp-nF1) on loperamide-induced constipation in rats. Constipation-induced male rats were treated orally with low to high doses of HLp-nF1 and an anti-constipation medication Dulcolax for five weeks. Study has 8 groups, control group; loperamide-treated group; Dulcolax-treated group; treatment with 3.2 × 1010, 8 × 1010 and 1.6 × 1011, cells/mL HLp-nF1; Loperamide + Dulcolax treated group. HLp-nF1 treated rats showed improvements in fecal pellet number, weight, water content, intestinal transit length, and contractility compared to the constipation-induced rats. Also, an increase in the intestine mucosal layer thickness and the number of mucin-producing crypt epithelial cells were observed in HLp-nF1-treated groups. Further, the levels of inflammatory cytokines levels were significantly downregulated by treatment with HLp-nF1 and Dulcolax. Notably, the metagenomics sequencing analysis demonstrated a similar genus pattern to the pre-preparation group and control with HLp-nF1 treatment. In conclusion, the administration of >3.2 × 1010 cells/mL HLp-nF1 has a positive impact on the constipated rats overall health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: IYK is a paid employee of Biogenics Korea. There are no patents, products in development or marketing products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
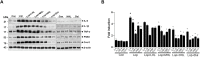

References
-
- Ibnou-Zekri N, Blum S, Schiffrin EJ, von der Weid T. Divergent patterns of colonization and immune response elicited from two intestinal Lactobacillus strains that display similar properties in vitro. Infect Immun. 2003;71(1):428–36. Epub 2002/12/24. 10.1128/iai.71.1.428-436.2003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

